|
Before you start implementing something, you need to make a plan. It allows you to assess strength, calculate what is needed and where and in what quantity. At the same time, strategic and operational planning are distinguished. We'll look at the objectives and goals for the second one. What is operational planning and how is it different from strategic planning? When studying something, you should start with terminology. Operational planning is an activity that consists in calculating the situation and drawing up development models for not short periods of time. It presents the planned works in the most detailed way. Operational planning is the final step in the overall process of calculating situations and drawing up development models. The key goal, which is pursued in this case, is to organize uniform production of products in specified volumes that meet quality criteria. What is the difference between strategic and operational planning? Speaking about them, a number of differences should be highlighted: - Operational planning is carried out by middle and lower-level managers, while strategic planning is the prerogative of senior managers.
- Operational decisions are routine and are made on a daily basis. Strategic ones require more preparation time.
- Operational planning does not provide for the development of an alternative option, while their presence is mandatory for strategic decisions.
- The operational considers only internal information sources, while the strategic is also interested in external ones.
This is the difference between them, generally speaking. You can, of course, delve into the details and consider all this more carefully, but this will already be a deviation from the topic. So let's move on to the next point. Methods and tasks of operational planning The basic goal that must be addressed is to organize the work of the company's employees in such a way that production is efficient. In addition, there are also such tasks: - Fulfillment of the set requirements for the quantitative and qualitative indicators of production.
- Effective use of working time.
- Creation of continuous production.
A number of methods are used to achieve and accomplish these objectives. There are four of them: - Volumetric method of operational planning. It is used to "break" the annual time period into shorter-term components. As a result, plans are allocated for a month, a week, a day, and even an hour. Its advantage is that the more detailed the planned volume of production, the easier it is to carry out the function of monitoring the efficiency of work. In this case, in addition to calculating "what and when", the optimization of processes at the enterprise is also carried out.
- The calendar method of operational planning. It consists in determining the specific dates for launching a certain product into production, as well as the end of its production. Although it can be adjusted if the market entry is successful. The calendar method is used to calculate the duration of the production cycle. This, in turn, forms the basis of the monthly workshop program.
- Mixed method of operational planning. Assumes union. In this case, both the duration of the production cycle and the amount of work performed over a certain period of time are planned. Used for combined activities.
- A dynamic method of operational planning. It is built on the consideration of a number of indicators, such as volumes, timing, production dynamics. It is believed that it is he who allows you to fully and reliably take into account the real capabilities of the enterprise. This method has one useful special tool - the customer order schedule.
Classification 
Operational work planning is divided into two main types: - By timing and content. In this case, the current and operational scheduling are distinguished.
- By scope. In this case, inter- and intradepartmental planning is distinguished.
The classification is different from the methods, keep in mind so as not to be confused. So, in this case, scheduling is the distribution of annual plans among departments. In addition, this also includes bringing the required figures to the performers of the work. As a basis, data such as the delivery time of products and the labor intensity of the work are used. Current planning implies the availability and regulation of the consumption of materials for the release of goods. Now to a different kind. Interdepartmental planning provides for the regulation of work by all shops. That is, if No. 1 has not made a blank out of materials, then No. 2 will not be able to produce products. In addition, there is the coordination of the activities of the support services. That is, if the warehouse is full, then there is no point in producing something for sale. Data such as master plan and order book are used as a basis. Intrashop planning is based on scheduling the work of production sites and production lines. This makes it possible to concretize and detail the production program. The objectives of operational planning pursued at the same time are to ensure uniform and uninterrupted production of products in certain quantities and for a specified time period, while observing quality standards and making optimal use of available capacities. In addition, a coordinating function is performed, thanks to which the well-coordinated work of the company's divisions is ensured. About functions Let's walk through what operational planning in an enterprise allows us to do: - Develop scheduling production standards. These include the size of the backlog, the size of batches, the duration of the production cycle, and the like.
- Calculations of the volumes of loading of areas and equipment.
- Drawing up operational programs for the main procurement and production shops.
- Implementation of management accounting and control over the implementation of plans.
- Operational regulation of production processes, timely identification of existing deviations from the targets, development and implementation of measures that will eliminate them.
Let's take a quick example. An operational plan is drawn up for the day. Constantly. Whereas accounting is a week late. The manager needs to know whether it is possible to conclude a contract for the urgent production of a product, whether there is capacity for this. He uses the capabilities of management accounting, contacting the head of the shop, and then decides that the urgent order can be taken (or not). There are great opportunities. The main thing is to use them. A competent organization of operational planning allows you to create an extremely useful and flexible system that has enormous potential. About the term and content 
Oh, how many points of view and approaches to solving certain problems exist. If the content and timing of work plays a role, then in this case there are two types of operational planning, the work with which is entrusted to managers and specialists: - Calendar. In this case, it means the distribution of monthly planned tasks to production departments, when special attention is paid to the deadlines. The established indicators are brought to the knowledge of specific work performers. With its use, shift-daily tasks are developed, and the sequence of work by individual employees is coordinated. In this case, the initial data are the annual production volumes, the labor intensity of the work performed, the timing of deliveries to the markets and other indicators of the socio-economic plans of the enterprise.
- Interdepartmental. It is used to ensure the development, regulation and control over the implementation of the set plans for the production and subsequent sale of products. Also, an important place here is occupied by the coordination of the work of the main and auxiliary departments, design and technological, planning and economic and other services.
So, in general, we have considered what the operational management of planning is. Consideration was conducted on separate points. But they act as part of a certain system, right? And what effect can be observed in this case? We will now look for the answer to this question. Systems in general 
Various elements are formed into one community. If everything is built adequately, efficiently and efficiently, then such operational planning systems show themselves very effectively, allowing them to successfully carry out activities. In the modern world, they are influenced by both internal factors of the enterprise and external market conditions. But let's formulate the very concept of a system for this case. This is the name of a certain set of various technologies and methods of planned work, which can be characterized by a certain degree of centralization, the order of movement and accounting of products (materials, raw materials, blanks), the object of regulation, the execution of documentation, the composition of the schedule indicators. All this is used to influence the course of the process of creating and consuming goods and services. The pursued goal of the system is to achieve the planned market results, spending on this the minimum possible amount of economic resources and working time. How can you characterize it? For this, the main indicators of the system can be distinguished: - The procedure for coordination, interaction and coordination of the work of sites and workshops.
- The accounting unit used.
- Techniques and methods for calculating indicators.
- The duration of the planning period.
- Composition of accompanying documentation.
- Methods for the formation of calendar tasks for the divisions of the enterprise.
The choice of a particular system depends on the demand for services and goods, expenses and planning results, the scale and type of production, the organizational structure of the company and some other points. A simple description without considering the most popular options is worth little. Therefore, the most famous operational planning systems will be considered. Such at the moment are detailed, piecemeal and custom-made. They are used both in small and medium-sized businesses, as well as in large companies. Detailed system Operational production planning of this type is suitable for a stable and highly organized commercial structure. This system is engaged in planning and regulating the progress of work, processes and technological operations for each part for a certain period, which can last an hour, a shift, a whole day, a week or even more. It is based on an accurate calculation of the rhythm and tact of the functioning of production areas and production lines. Also, this system is characterized by an adequate definition of technological, insurance, interoperational, transport and cycle backlogs. They must be constantly maintained at the calculated level during the production process. The use of a detailed system requires that high-quality scheduling and operational plans be developed, where there will be indicators of the volume of output, as well as the route of movement of the details of each item. Moreover, it is necessary to indicate all production stages and technological processes. Such operational planning of production is advisable to apply only in the presence of a stable and limited range of products being created, that is, with mass and large-scale production. Customized and packaged system 
Where and in what cases can they be applied? The order system is used when a single or small-scale production is carried out, where there is a diverse range and a small volume of products or services provided. In this case, a separate order acts as the main planning and accounting unit, which includes several works of the same type for a specific consumer. This system is based on the calculation of the lead rates and the duration of production cycles. Due to this, lead times are estimated for customer or market requirements. The complete system is used, as a rule, in serial engineering production. The basic basic accounting units use different parts that are included in the general set of goods or an assembly unit. Moreover, they are grouped according to certain criteria. Scheduling tasks for production departments are created not for individual names of parts, but for sets or groups. And so that they are enough for a unit, a whole car, the whole order or the agreed scope of services and works. Such a system makes it possible to reduce the labor intensity of planning and calculation work and organizational and managerial activities of employees of the functional and line services of the enterprise. The architecture of this system allows to increase the flexibility of operational planning, regulatory mechanisms and monitoring. And this, it should be noted, in conditions of market uncertainty, is an important tool for enterprises, which allows them to stabilize production. Brief description of subsystems Operational planning is a very voluminous subject of study. Therefore, alas, it will not be possible to consider all the points in detail. After all, this requires a book. But to mention it briefly is quite possible. We have already reviewed the three most popular options for operational planning systems. But they are formed from certain subsystems, right? This means that they should be given at least a few words. Operational and production planning provides for the presence of release tact subsystems, warehouse subsystems, in advance and a number of other processes and working moments. We will not consider all of them, for this is a great variety of material. But here's one you can study as an example. Let's talk about the warehouse subsystem. So, we have a production facility where the goods are made. For him, you must have a sufficient amount of wood. Suppliers are working as planned, supplying new boards, logs, sawdust - everything you need. A certain amount of stock is formed in the warehouse. It is calculated how many cubic meters of boards, logs and sawdust are spent on manufacturing products, and if there are problems with suppliers, then the time for which the accumulated stock will last. At the same time, in the operational plan, it is necessary to provide for suppliers to replenish the warehouse. Moreover, it is advisable to register contacts already in the document itself, or simply have an agreement. Operational and production planning in the considered example will prevent the stoppage of the processes running at the enterprise and avoid losses. Dealing with finances 
Cash planning should receive special attention. Why? Because without money, long-term activity is not possible. If they do not exist, then pay suppliers for resources and materials, and workers will not be able to pay for labor. And if at first it is still possible to agree on a small delay, then later ... In general, the enterprise will not continue its activities. Therefore, the operative is important, because with its help you can avoid more serious and unpleasant situations. For example, if a decade before the payment of wages it is clear that there will not be enough money to pay wages, then this means that you do not need to wait ten days, but do something. The specifics depend on the situation. If the strategy provided for the creation of a reserve fund for this purpose, then operational financial planning may provide that a certain amount should be taken from it. Didn't the management bother like that? Well, then you need to urgently look for someone to whom you can sell the goods / services, and in such a way as to keep within the available ten days. After all, if there is a long delay, then the labor inspectorate can get involved in the case, and there also the prosecutor's office. And it's better not to bother with their attention. There are quite a few options to deal with finances. If it is not possible to sell products and there is no reserve fund, then you can always turn to specialized organizations. For example, a banking institution. But in this case, it is better to have ongoing negotiations or another source that will cover the payments. Otherwise, the problems can only get worse. Conclusion 
So it was considered what constitutes operational planning. Let's go over the main points again. The main task that must be solved is to organize the work of the company's employees so that production is efficient. A number of methods and systems can be used to achieve this. Ideally, if it is possible to reduce production defects, economically use resources, optimally load production facilities, technological equipment and workers. It should be noted that planning as a management function is closely related to organization, motivation, coordination and control. Therefore, it is better to consider it in practice not separately, but as a component of the whole complex. This point of view will allow you to avoid various unforeseen and unpleasant moments. After all, if it is calculated how much resources are needed, but the situation for the coordination of workers is not outlined, then it may turn out that the plan is not as good as it was initially thought.
AND TECHNOLOGICAL DOCUMENTATION
OPERATIONAL PLANNING OF PRODUCTION
The essence of operational planning. Operational planning of the production of procurement enterprises. Calculation of the output of semi-finished products
The essence of operational planning is to draw up an enterprise program. Production program planning issues are dealt with by production managers (deputies), heads of production departments, foremen, and accountants. To draw up the production program of the procurement enterprise, the following data are required: the range of products (semi-finished products, culinary products, flour confectionery products); technical equipment of the enterprise; a network of catering establishments and a retail network that have entered into contracts with a procurement company or specialized procurement shops; the range and quantity of products required for these enterprises; the volume of semi-finished products produced by food industry enterprises for pre-food enterprises.
Operational production planning is carried out in a certain sequence, therefore, at each stage there is no
it is necessary to create certain organizational conditions conducive to the correct organization of the technological process, the rational organization of labor, and the clear performance of each employee of their duties.
An important place in the operational planning of production is occupied by the dispatch service. Operational planning of the production of a procurement enterprise and specialized procurement shops is carried out in the following sequence. Enterprises with which a contract has been concluded make daily orders for semi-finished products, culinary and flour confectionery products and transfer them to procurement enterprises in dispatching services (departments). Orders received in the dispatch service are summarized for all types of products and transferred to the shops in the form of a daily production plan. One copy of the order is sent to the expedition for subsequent order picking. Applications are accepted the day before their execution. This is due to the fact that the production department needs to get the required assortment and quantity of raw materials and products in advance for the implementation of the technological process of manufacturing products on demand.
Semi-finished products and culinary products are produced in accordance with TU, OST, as well as the data of the Collection of norms for waste and losses during cold and heat treatment of raw materials.
At the procurement enterprise, in order to monitor the correct use of raw materials and the amount of semi-finished products produced, the head of the shop draws up an act for cutting the mass of raw materials into large-lump semi-finished products according to Form 61. The act specifies the name and quantity of raw materials received by the shop in natural and value terms, the output rates of large-lump semi-finished products according to The collection of recipes in percent and kilograms. The act is signed by the head of the shop, checked in the accounting department and approved by the director of the enterprise.
The work of the confectionery shops is carried out in accordance with the planned production output. Based on the raw materials and orders available in the pantry of the enterprise, the head or foreman of the confectionery department draws up an order-order in form 76 (Table 2). A work order is a document for calculating a production task for the manufacture of products to order: determining the need for raw materials. The work order serves as the basis for the release of raw materials from the pantry for production.
Operational planning in enterprises with a full production cycle
The catering establishment must approve a monthly turnover plan, on the basis of which the production program for the day is drawn up.
In restaurants, where the assortment of dishes is very large, the menu mainly includes customized a la carte dishes, so it is difficult to plan in advance the number of dishes produced, but, taking into account the past experience, in a restaurant it is possible to plan the release of the number of semi-finished products (when processing meat, poultry, fish) and how much food you need to get from the warehouse per day.
At catering establishments with a certain contingent of consumers (canteens at industrial enterprises, educational institutions, childcare facilities, rest homes, etc.), it is possible to more clearly plan the production work for every day.
Operational planning of production work includes the following elements:
Drawing up a planned menu for a week, a decade (cyclical menu), on its basis the development of a menu plan reflecting the daily production program of the enterprise; preparation and approval of the menu;
Calculation of the need for products for the preparation of dishes provided for by the menu plan and drawing up requirements for raw materials;
Registration of a bill of lading for the release of products from the pantry in production and receipt of raw materials;
Distribution of raw materials between workshops and definition of tasks for cooks in accordance with the menu plan.
The first stage of operational planning is the preparation of a planned menu, the presence of which makes it possible to ensure a variety of dishes on days of the week, to avoid repetitions of the same dishes, to ensure a clear organization of the supply of raw materials and semi-finished products, timely sending applications to wholesale depots, industrial enterprises, to properly organize technological cooking process and labor of production workers. The planned menu indicates the assortment and number of dishes of each item that can be prepared at the given enterprise on days of the week or decade. When drawing up a planned menu, the qualifications of cooks, consumer demand, the possibility of supplying raw materials and the seasonality of raw materials, and the technical equipment of the enterprise are taken into account.
The second and main stage of operational planning is the preparation of a plan-menu by the production manager on the eve of the planned day (no later than 15 hours) and its approval by the director of the enterprise. It contains the names, recipe numbers and the number of dishes, indicating the timing of their preparation in separate batches, taking into account consumer demand.
The main factors that must be taken into account when drawing up the menu include: the approximate range of products recommended for public catering enterprises, depending on its type and type of ration provided, the availability of raw materials and its seasonality.
An approximate assortment of dishes (assortment minimum) is a certain number of names of cold dishes, hot dishes, drinks typical for various catering establishments (restaurants, canteens, cafes, etc.). When drawing up a menu plan, it is necessary to take into account the availability of raw materials in the pantries and its seasonality. Dishes and snacks included in the menu should be varied both in the types of raw materials and in the methods of heat treatment (boiled, stewed, fried, stewed, baked); the qualification composition of workers, production capacity and its equipment with trade and technological equipment, as well as the labor intensity of dishes, that is, the time spent on preparing a unit of production, are also taken into account. When approving the menu plan, the director and production manager are responsible for ensuring that the dishes included in the menu are on sale throughout the entire day of the company's trade.
In catering establishments with a free choice of dishes, operational planning begins with drawing up a menu plan for one day in accordance with the turnover.
Types of menus, their characteristics
Menu - a list of snacks, dishes, drinks, flour confectionery products available for sale on a given day with an indication of the output and price - must be signed by the director, production manager and calculator. Depending on the type of enterprise and the consumer contingent served, various types of menus are developed: with a free choice of dishes; set lunches and dinners by subscription; daily diet; dietary and baby food; banquet.
Free choice menu compiled at public catering establishments (in restaurants, bars, canteens, cafes, snack bars). This is a list of dishes, written in a specific order, indicating the output of dishes, side dishes, main product and price. For the first courses on the menu, as a rule, the price of a portion and a half portion is given. The menu of the restaurant does not indicate the output of dishes.
When drawing up the menu, they adhere to certain rules for the arrangement of snacks and dishes.
Industrial management (5)Abstract >> ManagementSelf-realization of personality in production process. 4. Principles production management Methods Listed ... of Organization production processes. Industrial management should provide high results production-economic ... Industrial management (2)Abstract >> ManagementReflection in such a scientific discipline as industrial management. Industrial management Is a science that studies management ... Institute of Informatics. - M .: INFRA-M, 2003 .-- 574p. Industrial management: textbook for universities / S. D. Ilyenkova, A. V. ... Industrial management (4)Abstract >> Management... production structure (sufficient and limited composition production subdivisions); lack of duplicate production links; ensuring direct flow production... objects of a derivative management... Increasing the level of use ... Industrial management (6)Abstract >> ManagementAnd etc.); stages of definition (design, production and operational); method of determination (calculated, ... physiological, psychophysiological properties of a person, manifested in production and household processes; aesthetic indicators, ... -
Introduction
Since the 1970s, planning methods have been enriched and improved at an accelerating rate. Two factors play a special role in this. The first is the economic crises of the last quarter of the 20th century. They forced economists and managers from different countries to find new adequate management methods. The second factor is associated with the rapid spread of information technology and computer technology. These tools made the analysis of the prospects for the development of the enterprise and their forecasting publicly available. The creation of information systems in enterprises has made it possible to automate, simplify and accelerate the implementation of a huge number of planning and control functions.
The abandonment of an ineffective command and control system was perceived by many managers and specialists as an opportunity to abandon planning altogether. However, this approach is destructive, its results are usually deplorable. Underestimation of planning is one of the reasons for the ruin and bankruptcy of an enterprise.
The purpose of planning as a management function is to strive in advance to take into account, if possible, all internal and external factors that provide favorable conditions for the normal functioning and development of the organization. It provides for the development of a set of measures that determine the sequence of achieving specific goals, taking into account the possibilities of the most efficient use of resources by each production unit and the entire organization.
On-farm planning is planning within an enterprise. Its main goal is to improve the efficiency of the enterprise. This task is being solved through the development and implementation in practice of strategic, current and operational plans.
Operational planning consists in the development of the most important volumetric and calendar indicators of production and economic activity. At the same time, the means and methods of solving problems, the use of resources, the introduction of new technology are being developed in detail.
The relevance of the chosen topic is confirmed by the fact that operational planning is an intermediate link on the way to achieving strategic goals and objectives.
The object of the research is JSC APK "Biryuchensky".
The purpose of the course work is to consider the features of operational planning of production of products at the enterprise of JSC APK "Biryuchensky" and the formation of a set of measures to improve the efficiency of its activities.
To achieve this goal, it is necessary to solve the following tasks:
to reveal the essence and content of the theoretical foundations of operational planning at the enterprise; to analyze the state of the main economic indicators at JSC APK "Biryuchensky"; to propose the main directions of increasing the efficiency of the activity of JSC APK "Biryuchensky".
When writing the term paper, the following were used: primary and reporting documents of the organization, scientific literature, articles by scientists, periodicals, collections.
1. Theoretical foundations of operational planning at the enterprise
Operational planning of production consists in the development of the most important volumetric and calendar indicators of the production and economic activity of the enterprise. Any process of operational planning provides for the implementation by economists-managers of such stages of activity as the choice of a strategy for the development of an enterprise, substantiation of the form of organization of production, determination of a logistic scheme for the movement of material flows, development of basic scheduling standards, operational planning of the work of production units, organizational preparation of production, direct organization operational work, monitoring and regulation of the course of production. The main task of operational planning ultimately comes down to ensuring a well-coordinated and rhythmic course of all production processes at the enterprise in order to maximize the satisfaction of the basic needs of the market, rational use of available economic resources and maximize profit.
In operational planning of production, depending on the indicators being developed, such basic methods are used as volumetric, calendar, as well as their varieties: volumetric calendar and volumetric dynamic.
The volumetric method is designed to distribute the annual production and sales of the company's products to individual departments and shorter time intervals - quarter, month, decade, week, day and hour. This method provides not only the distribution of work, but also the optimization of the use of production assets and, first of all, technological equipment and assembly areas for the planned time interval. With its help, monthly production programs of the main shops are formed and the timing of product release or order fulfillment in all manufacturing divisions of the enterprise is planned.
The calendar method is used to plan specific time frames for launching and releasing products, standards for the duration of the production cycle and ahead of time in the production of individual works relative to the release of head products intended for sale in the relevant product market. This method is based on the use of progressive time norms to calculate production cycles for the manufacture of individual parts, planned sets of products and the implementation of assembly processes. In turn, the production cycle of the main product serves as a regulatory framework for the formation of draft monthly production programs for the rest of the manufacturing shops and sections of the enterprise.
The volumetric calendar method allows you to simultaneously plan the timing and volume of work performed at the enterprise as a whole for the entire specified period of time - a year, a quarter, a month, etc. With its help, the duration of the production cycle of release and delivery of products to the market is calculated, as well as the indicators of the loading of technological equipment and assembly stands in each division of the enterprise. This method can be used to develop monthly production programs for both producing and non-producing workshops and sections.
The volumetric dynamic method provides for close interaction of such planned and calculated indicators as the timing, volumes and dynamics of production of products, goods and services. In market conditions, this method allows the most fully to take into account the volumes of demand and production capabilities of the enterprise and creates a planning and organizational basis for the optimal use of available resources at each enterprise. It involves the construction of schedules for the fulfillment of consumer orders and the loading of production sites and manufacturing shops.
The purpose of operational planning is to achieve production output within the timeframes specified by business contracts. To achieve this goal, it is necessary to plan the timing of the production of orders, it is also necessary to organize a well-coordinated, rhythmic work of all sections and workplaces.
As part of the implementation of the main goal, the agro-industrial complex faces the following planning tasks:
determination of existing and prospective needs of buyers, analysis of the ways of using these products, research of patterns of purchasing behavior in the respective markets; forecasting possible sales volumes of products, selling prices, production costs and profitability of economic activity; determination of the enterprise's need for material and technical resources and their effective distribution across industries and divisions of the enterprise; determination of the financial capabilities of the enterprise for the implementation of the production program adopted for execution; ensuring a strategy of specialization, cooperation and integration of production; projecting of the nearest and long-term perspectives according to the periods of execution; organization of the execution of the plan and control over its execution; solving problems of social development of the labor collective, private household plots of the population, economic problems and rational use of natural resources; target orientation and coordination of the enterprise; identifying risks; unbundling and thereby simplifying the level of problems; increasing flexibility, adaptability to changes; achieving consistency, proportionality, rhythm, continuity (flow) of production based on the balanced development of the main industries of the enterprise.
The operational planning functions include:
development and control of the implementation of planned targets for the release of products in kind for workshops, sections and workplaces for a month, decade (or week), day, shift. control over the material and technical support and technical preparation of production, since in order to start production of products within the time specified by the task, it is necessary to have materials, blanks, tools, tooling, technological documentation at the workplace. It is necessary to ensure the operational reliability of equipment and other technical means. Checking the availability of everything necessary for the production of products is carried out by the operational planning services. achieving a uniform load of equipment, jobs. Taking into account the requirements of the market, operational planning should be flexible - to respond in a timely manner to the arrival of new orders, to include them in the plan on time, to take into account the changing priorities of the production of products. In other words, it must be open to the production of new orders. accounting and tracking the progress of production along the entire chain of the production process, dispatch control and regulation of the production progress.
According to the scope of the production process in space, a distinction is made between factory and workshop operational and production planning.
The plant OP covers the development and control of operational plans for the plant as a whole, broken down by shops and is carried out by the production planning or dispatching department (PDO) of the plant management.
The workshop OP is associated with the development and control of operational plans for the workshop as a whole, broken down by areas and workplaces, and is carried out by the production planning or dispatching bureau (PPB or PDB) of the workshop.
Operational and production planning includes two
related parts: scheduling and scheduling.
Scheduling includes:
development of scheduling standards; development of operational plans; development of shift-daily tasks.
Operational production planning serves to concretize the annual marketing plan for the production of products in physical terms and begins with an analysis of the annual production plan.
Monthly and ten-day plans provide for the distribution of tasks by day and remain flexible and open for any of the following days. The schedule of the current day (shift-daily task - CVD) tends to be kept closed for any changes, i.e. it becomes a tough assignment for the whole day. However, during the day, situations may arise when it is necessary to urgently complete a task or carry out work to correct a marriage. In view of this, time reserves should be provided for in the operational and calendar plans. If there are no reserves in the schedule, then urgent tasks delay the release of the planned ones. An undesirable situation is created, which must be taken into account by the task of the next day and the redistribution of priorities for the execution of various tasks.
The topic is banal, but the collective mind of any company can easily lose the thread and get tangled in three birches ...
So, what is an operational plan within a strategic holding (according to one of the well-known classifications) ...
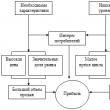
Abbreviations: FR - functional manager, DK - subsidiary company, MC - management company, EDMS - e-mail system. workflow, DSR - director for strat. development
INITIAL CONDITIONS for reasoning
- The concept of "operational plan" is considered within the framework of a strategic holding.
- An operational plan is an operational management tool.
- The criterion of the operational plan is the detailing of work for a time horizon of a month, not more than a month.
- Operational plans are a more detailed development and specification of the initially developed and agreed annual functional work plans.
- The company's annual schedule of key events reflects the agreed annual functional work plans.
- It is necessary to distinguish between operational control and operational plan. Operational control of strategic plans (in case of force majeure, a crisis situation) and control of operational plans are two different things.
WHAT IS THE OPERATIONAL PLAN?
- This is a plan of work, activities, tasks, assignments, implemented by an employee within a calendar month. At the end of the current month, the operational plan for the next month is specified.
- Weekly working out of the plan within a month, weekly / monthly monitoring within the DC.
- Operational plans should be a more detailed breakdown of the annual functional work plans. It is formed on the basis of the annual work plan. Initially, the agreement of the annual functional work plans is achieved. For critical tasks, the consistency of the operational plans of employees should be automatically ensured, due to the consistency of the annual work plans. At operational meetings, the details of annual plans for the monthly horizon are specified.
- Operational plans should be consistent with annual plans. In case of force majeure, all annual plans for the remaining period and operational plans for the next month are adjusted.
- The implementation of operational plans ensures the implementation of the business processes of the DC, the successful implementation of operational plans ensures compliance with the standards of process (operational) indicators, as a condition for achieving the strategic goals of the company. Operational indicators and operational plans are tied to the standards of business processes.
The operational plan of FD DK SHOULD NOT include project tasks, since even control of an individual project milestone should be carried out with an understanding of the state of the entire project as a whole, and with an understanding of the consequences of the implementation of one project milestone on subsequent related project tasks.
The operational plan contains:
- Tasks from annual plans (Business plan) in the context of the month, - functional tasks within the responsibility and job duties of the employee.
- Protocol assignments and tasks from the top management of the DC and CM.
The annual functional plans of activities and operational plans MUST reflect the regularly performed job responsibilities and functions, with the only difference that:
- In CI, the functional of an employee (FD DK) is defined in general, - by types / groups of work, without specification;
- And in the action plans, the content of the work is concretized (specific media outlets, agencies, etc.) and is tied to calendar dates and budgets,
- in the annual work plan, large blocks are defined, for critical events, the work is detailed on a monthly basis,
- the operational monthly work plan is detailed weekly, critical events are scheduled by day.
CONTROL OF OPERATIONAL PLAN EXECUTION. INTERACTION OF UK-DK IN PART OF DEVELOPMENT AND CONTROL OF OPERATIONAL PLANS
The operational plan in the DC is a tool for the operational management of the business for the State Duma, the DK FR, on which the CM should not have a direct administrative impact on a daily / weekly / monthly basis. For the corporate center of the holding, which wants to be a "strategic holding", there should be enough interaction on the quarterly reporting, and on its results - the subsequent adjustment of the annual plans of the management company and DC for the remaining period.
The DK's operational plan SHOULD NOT be under the President's control.
At monthly meetings with the participation of the President, there is an OPERATIONAL CONTROL of the implementation of the company's strategic plans in order to summarize intermediate results, make the necessary management decisions, including adjusting further actions, if there is an urgent need for this (a critical event, force majeure). Otherwise, we are not a strategic holding, but an operating holding, and all gene. directors, DEMs, DCs, etc. must be transferred to the UK.
Ideally, each manager should have an annual plan detailing the operational plan for the next month, and detailing the work for his subordinates.
The coordination of the annual work plans with a monthly breakdown should be carried out by two managers - the State Duma of the DC and the FR of the Criminal Code.
The approval of the operational plan should be carried out only by the State Duma DK.
It is advisable to formulate schedules for general corporate projects and annual functional plans within the framework of business planning, so that FCs' FRs can take them into account in a timely manner when developing their annual plans.
Monitoring: FC PM must have access to view the current annual plans of FC FC, and control it only in terms of general corporate tasks (its area of responsibility).
WHAT TOOLS SUPPORTED THE EVENT PLANNING SYSTEM: ANNUAL PLANS, OPERATIONAL
- Ideally, both development projects and functional annual plans (detailed down to operational ones) should be in a single database (DB) with uniform characteristics:
- Centralized employee directory;
- Unified calendar with weekends and holidays;
- A common vacation calendar for all employees - which will allow, when planning for a year, not to overload employees, avoid rushwork and downtime when someone goes on vacation;
- Possibility of notifications on critical deadlines, critical events (order execution control system);
- Risk analysis - An analysis of the critical path to plan implementation.
- This solution can be, for example, the server version of MS Project. This solution will provide a clear consistency of annual, operational work plans, and projects - consistency in terms of time, by executors, by the workload of employees. If you need to adjust one plan - then you can assess the consequences - how the adjusted plan will affect the other plans associated with it.
- Traditional IT benefits: community access, access rights system, single event entry, history preservation.
TRANSITION PERIOD (TRANSITION AS AN OPTION TO SERVER MS PROJECT)
Annual plans and their detailing within the framework of operational plans can be kept in an Excel file in the EDMS with general access for top managers.
MOTIVATION SYSTEM FOR THE RESULTS OF THE IMPLEMENTATION OF PLANS
At the end of the annual reporting period, the results of the annual work plan are assessed in conjunction with the implementation of target indicators (strategic team, individual):
- The assessment of the manager in the motivation card in terms of general corporate tasks is divided into two parts: the assessment of the PR of the Criminal Code and the assessment of the GD of the DC with certain weights and is carried out independently, directly affecting the amount of the bonus (with an agreed weight).
There will be questions - I will be glad to talk, especially when in practice there was a need to achieve a common understanding of methodological things by the collective mind
Strat Director development of the DC is responsible for coordination, organization in the processes of strategic and business planning,
but here's an unexpected question - who is responsible for the processes of operational planning, control, and the operational management system as a whole? Is it Gen. dir.? JEM also does not want to be a "boot" .. And where there is no coordinator such as JEM - they ask from the Fin. director ...?
|