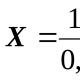Sections of the site
Editor's Choice:
- First flocks of migratory birds of the year
- New Year's sock and many other wonderful polymer clay crafts
- Who is a carpenter and what does he do: a centuries-old profession Advantages of the profession of a carpenter
- Promotional codes for the discount "Yulmart"
- Statuses about life with meaning
- Tip of the day: what to do if a thing is spoiled in dry cleaning
- How much is an hour of work?
- Miracle, originally from the USSR - soap for all occasions
- How to calculate discount. How to calculate percentages. Where do nassamihs live
- Regulations on wages
Advertising
| Regulations on wages and bonuses of the bank. Regulations on wages |
|
In 2019, officials and judges announced new rules for calculating salaries. The experts prepared samples of entries in the regulation on remuneration according to the new rules and told how to develop and approve the document. From the article you will learn: Download related documents: Regulation on remuneration: specify the new rulesThe calculation and payment of salaries, allowances and bonuses is an important aspect of the activity of any enterprise, strictly regulated by law and local regulations. In order to establish a unified procedure for settlements and effectively interact with staff on remuneration issues, it is recommended to develop a special regulatory act. Note that the provision on the remuneration of employees is not considered a mandatory document from the point of view of the law. The official salary, dates of payment of salaries and other conditions can also be prescribed in the employment contract, and the rules for calculating bonuses and compensations in the collective agreement. But the presence of a single document with clearly formulated algorithms for remuneration reduces the risk of conflict situations. Crib. How to specify the components of the salary in the employment contractin 2018, personnel officers massively made changes to the regulation on remuneration. This is due to the new rules for calculating wages and the new resolution of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation on new rules for the payment of additional payments to (Resolution of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation dated June 28, 2018 No. 26-P). Important changes that need to be made to the Regulations on wagesChange #1. Rewrite the clause on employee bonuses The phrase about the calculation of additional payments from the salary is now considered a violation. This applies to cases where, in addition to the salary, employees receive permanent, for example, for intensity, for knowledge of a foreign language. The Constitutional Court, in its ruling of June 28, 2018 No. 26-P, noted that the Labor Code establishes the minimum wage for work on a weekend or holiday. But this does not mean that other allowances should not be taken into account. Rostrud extended this rule to pay for work overtime and at night (answer dated 08/02/2018 on the site onlineinspektsiya.rf). Change #2. Change the point about comparing wages with the minimum wage due to overtime Overtime hours are not included in the minimum wage (Letter of the Ministry of Labor dated September 4, 2018 No. 14-1 / OOG-7353). It is possible that your pay statement does not specify which payments are summed up for comparison with the minimum wage to calculate the additional payment to the minimum wage. Write it like this: “The salary for a month of an employee who has fully worked out the norm of working hours and fulfilled the labor norm cannot be lower than the minimum wage. If the salary of an employee who has fully worked out the norm of working hours for this period and fulfilled the labor norm is lower than the minimum wage, he is charged an additional payment up to the minimum wage. When calculating the supplement to the minimum wage, the amount of payments for comparison with the minimum wage does not include payment for overtime work. Change #3. The district coefficient and the northern allowance can no longer be included in the minimum wage The Constitutional Court, in its decision of December 7, 2017 No. 38-P, established that the district coefficient and the percentage allowance cannot be included in the minimum wage. This decision came into force immediately, which was confirmed by the Ministry of Labor in a letter dated 06/04/2018 No. 14-1 / 10 / V-4036. Therefore, if the old norm is in force in your Regulation, remove this paragraph from the document. Regulation on remuneration: sample documentLabor legislation does not establish a standard form of the Regulation on remuneration, therefore, an organization can draw it up in any form, taking into account the specifics of its activities. As a rule, the Regulations on remuneration and bonuses for employees include the following sections: Table. What sections to include in the Regulation on remuneration
Standard sections can be modified or removed. For example, if you need to develop for a security company that does not practice the payment of material assistance to employees, the regulation on labor protection is drawn up without the seventh section. The company using bonus clause, can safely exclude the sixth section of the template so that the regulations are not duplicated even partially. Important! When compiling a document from scratch, it is easy to miss an important detail or incorrectly calculate the timing of the payment of salaries, which, according to the law, must be paid strictly twice a month. Table. Terms of payment of salaries
Often overlooked is the rate of wage indexation. Organizations determine the procedure for indexing salaries independently. It may correspond to the officially established consumer price index for the whole country or in a separate region, the rate of inflation, the growth of the subsistence level of the able-bodied population, or other indicators that reflect the rise in prices for goods and services. Regulations on wages (fragment). Salary indexation
How to agree and approve the regulation on remuneration and bonusesThe draft document is not approved immediately. First, it must be agreed with the officials responsible for calculating and issuing wages to personnel: the chief accountant, the head of the financial department, and the head of the personnel department. If the organization has a trade union or any other association representing the interests of workers, one more stage is added. Any local acts related to wages should be agreed with the trade union in the manner prescribed by Article 372 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. And only after a positive decision of the trade union, the position is sent for approval to the head of the company. After agreement with the representative body, the Regulations should be approved by the head of the organization. There are two ways to approve a document - issue a separate order or affix the appropriate stamp on the document itself, at the top of the sheet. Then familiarize te with the text of the Regulations of the employees of the organization under the signature (part 3 of article 68 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). To do this, you can, in particular, maintain a sheet of familiarization of employees with the Regulations, where employees will put their signatures. How to indicate bonuses in the salary statementIf the employer has not developed a separate provision on bonuses, it is worth adding the corresponding section to the regulation on remuneration. Using the standard template, make the necessary additions to the bonus section. Write down the conditions for bonuses, indicate how much bonuses are paid and how regularly this happens. The more transparent the bonus system, the more accurate the wording used, the less the risk of claims from employees who felt that they were unfairly deprived of the bonus or paid it insufficiently. Make sure that the section on incentive payments reflects:
Do not forget to familiarize all employees with the document under the signature in the familiarization sheet or a special journal. The employer himself decides which system of remuneration to fix in the Regulations on remuneration. So that neither the labor nor the tax inspectorate makes claims about the procedure for paying wages, clearly state the condition on the timing of the payment of wages and on the indexation of wages. Familiarize employees with the adopted Regulations for signature. The regulation regulating the basic principles of remuneration of employees - legally enforceable document. It combines the dynamics, specifics and temporal parameters of payments adopted by the enterprise, organization, the principles of material accruals, methods of indexation and other important issues related to cash settlements between the two parties of the labor process - the employee and the employer. Why is it necessary and whether it is possible not to issue
Its purpose is not just to indicate in writing the principles and systems used for accruing cash settlements with employees, which are a legitimate measure of remuneration for the work they have performed. An equally important task is to legally fix the incentive procedure and the rules for material remuneration of people. If we consider the issue from the point of view of legal state policy, the document sets itself the task of fixing in paper form all the accepted and applied in practice mechanisms for remuneration for the labor activity of the team. The main function of paper is informational. It consolidates all actions aimed at receiving monetary remuneration by employees for their work in any of its forms and manifestations. If the enterprise is large, has branches, this document may consist of hundreds of pages. In this case, its structural division into volumes is carried out. The paper determines the legality of entering labor costs into tax items, while the absence of such a document will reduce by an order of magnitude chances, in the event of disputes with the tax authorities, to prove to them that they are right in controversial issues. For example, in the reduction of the base rate for the collection of income or premium tax. Taking into account these and other advantages that this act gives, administrations, as a rule, are interested in its existence and do not spare the resources and time spent on its creation. The employer, relying on the points of the document, uses the procedure for settlements with the team prescribed in it in such a way that the application of the policy of unfair distribution of the wage fund between staff units becomes impossible. The principle of objective encouragement and legal justification of all forms of remuneration for each individual employee is working. The presence of a provision does not make much sense only if all the principles of payroll are spelled out in detail in the labor agreement between the employee and the employer, with a description of all the nuances and force majeure circumstances of the labor process. Legally, punishment for the absence of an act or the procedure for its preparation is not provided. What will be its form depends on the specifics of production and the wishes of the manager.
The act should be classified as an internal legal normative document. It is approved by the administration of the company with the mandatory participation of the director and chief accountant. In the development and drafting of the main provisions of the provision should take part the following persons:
Features of combining salaries and bonusesRegulatory framework of Russian legislation does not prohibit Consolidation of salaries and bonus accruals to employees. It is recommended to do it in a way that is acceptable, and most importantly, convenient for each specific organization. Thus, at various enterprises one can observe multiple forms and options for drawing up a provision, which are based on the procedure for calculating material payments to employees. It is possible to issue this document in the form of a basic manual that regulates only issues directly related to accruals for payment of work performed, according to the labor agreement. At the same time, the main points regarding the procedure for bonuses are drawn up in a different provision. Accordingly, in this case, for each form of accrual, there should be accompanying internal acts. A fairly popular step in the management policy of enterprises is adoption of a collective agreement- it describes in detail all the material nuances of bilateral relations in the aspect of the employee-employer. If the directorate decides on a single document, its content should include points:
Information on wages and bonuses must be compiled in such a way that any full-time employee, having familiarized himself with it, can understand where the amount of money and bonuses that he receives for his work come from. By the way, according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, this information should be transparent and open for review by all employees of the company. Within the framework of the current Labor legislation, it is mandatory to include in the provision the following main points:  Tabular part of the positionAll surcharges must be made in the appendices, designed in the form of tables. And although this requirement is not considered mandatory (the text form is also applicable), this method of submission more preferred. The table where the calculations for surcharges are written includes those funds that exist in the enterprise other than wages. For each of their types, the current interest rates are entered in the appropriate column - overtime, night, holidays. IN column "Notes"(it is usually at the end) paint explanatory comments, for example, hours worked at night. Compensation transfers are processed in the same way. Additions are entered under each category of payments indicating the amount in figures and words and a mathematical algorithm or formula, based on which this result was obtained. For example, harmful conditions at work transferred to an employee at the time of his dismissal will depend on a number of factors, which are converted into the calculation algorithm. A table including allowances is only necessary in situations where such a material financing arrangement takes place in this organization. For example, this is an allowance for years worked in one place. This paragraph implies a full explanation of the time frame during which this accrual is due and carried out. Approximately in this way, other tables are compiled, the number of which is determined by the needs of production activities and the specifics of settlements with employees. Need for an annual review
For example, an organization introduces new technologies, expands the scope of its activities. In such situations, it will certainly be necessary to attract new personnel, respectively, there will be professions for which it will be necessary to revise or re-adopt the procedure for calculating cash payments. In the effectiveness of the document, as a rule, both sides of the process are interested- employees and administration of the enterprise. For this reason, it is extremely important to maintain them in working condition - timely revision, adoption of amendments. In addition, the planned adjustment of the greetings to the general systematization of the internal document flow, since it is its main part, will simplify the control of the activities of both individual structures and the organization as a whole. Keep track of the current state of the act - direct responsibility of the director of the enterprise. To accomplish this task, most often, a revision of the provision on material payments to employees is carried out. The nuances of piecework payThe regulation on the remuneration of employees should take into account following points concerning the specifics of financing this type of work:  All items that are indicated in the act and relate to this form of payment must be agreed upon at a general trade union meeting of the collective. This is enshrined in article 135 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. Often there are situations when the size of the tariff size changes. In this case, an appropriate amendment is made to the current regulation and again submitted for general collective discussion. Shelf lifeEach internal document has its own storage periods approved by the current legislative acts. To improve the quality of understanding of all aspects of the organizational activities of the enterprise, the storage period for the provisions on remuneration of employees has been increased up to 75 years. For proper preservation, in addition to the paper version, it is necessary to have electronic copy. It is important to understand that from a legal point of view, the calculation of the starting date of the specified period falls on January of the year, which follows the reporting period in which the clerical work was transferred to the archive department according to the situation. If the regulated storage periods are violated through the fault of the company administration, it will be subject to penalties which are quite large in size. What should be in the Payroll Regulations? The answer to the question is in this video.
Regulation on remuneration - an internal regulatory act of the organization, which indicates complete information on wages. We'll show you how to make it. The regulation on remuneration and material incentives fixes the main characteristics of the remuneration of employees:
In other words, this document regulates how employees are paid in a particular organization. Is a document required?The legislation does not establish the obligation to draw up a Regulation on the remuneration of employees. But at the first tax audit, the employer understands its importance. It is this document, if it exists, that makes it possible to prove the legitimacy of reducing the tax base for income tax or STS. And any institution is interested in this action. From the employee's point of view, the availability of such information makes the system of remuneration and rewards more transparent. This ensures the attractiveness of the organization as an employer and prevents a shortage of personnel. Is it possible to do withoutThe GIT will not be able to punish an enterprise if it does not have a Regulation on remuneration for 2020: no new rules or penalties have been established for this. Sometimes its development is redundant:
How to enter a positionThe management is engaged in the development of a local regulatory act. But the sole executive body does not have the right to adopt the Regulations on wages and bonuses for employees. In accordance with article 135 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, any internal regulatory documentation affecting wages must be approved by the trade union (of course, if it is at the enterprise) If there is no such body in the company, accordingly, there is no need to approve the Payment Regulations. When a compromise is reached, the leader issues an order. In it he reflects:
From the date specified in the order, the Regulations on wages come into force. It is signed either by the head (for example, the general director), or by a person with the appropriate authority - by proxy. So, you should make sure that the latter is valid at the time of signing. Familiarization of all employees under signature with the Regulation on remuneration, introduced again or already existing at the enterprise, is mandatory. There are several ways to do it right:
What to include in the provisionUsually the number of points depends on the number of wage systems used, additional payments and other specifics of a particular organization. Sometimes the consideration of individual issues is taken out in separate sections (for example, “Payment systems” are not considered in the “General Provisions”, but separately from them, as a separate part), or they are listed in the water part - this option illustrates a sample provision on remuneration and bonuses for employees .
The legislation does not contain a strict form for this case. The standard document includes the following sections:
The approximate regulation on the remuneration of employees of budgetary institutions for 2020 will be much more voluminous than for a trading company. The salary of a state employee is a complex system, and all its components should be described in detail. Types of cash incentivesThe regulation includes an important section on monetary incentives for employees. It must indicate all the current types of compensation and allowances with a specific indication of their amounts and the procedure for payment (in which cases they are applied and in what amount). The reward system may also include the provision of free tours, tickets, etc. - then information about this is included in the document. In the "Material Assistance" section, you must specify a complete list of cases when the administration provides financial support to its employees. This list usually includes: the birth of a child, the loss of a close relative, marriage. You can also talk about the case of individual assistance based on specific circumstances. Additional items are added as desired. If you decide to use the 2020 employee remuneration clause prepared by experts, you should carefully double-check it for compliance with the procedures of your organization and rework it: for example, some allowances are provided, but some are not. Some set a limit on the total amount of co-payments, others do not limit them. It is necessary to indicate the specific amount of material assistance or the method of its determination. For example, the director establishes it by his own decision in a separate order based on the submission of the immediate supervisor of the employee. Also in this paragraph, it is separately indicated whether the amount of material assistance will be taken into account when calculating average earnings. Changes and storageAll changes are made by order of the management. It is drawn up according to the same rules as in the case of approval. It must contain the following information:
If the changes affect the amount of wages, then each employee is warned about them personally. Notifications are sent out 2 months in advance. Although we are talking about an internal regulatory act, the period of its storage is strictly regulated. According to the Order of the Ministry of Culture dated August 25, 2010 No. 55, the Regulation on wages belongs to category No. 4 - documents related to accounting and reporting, and not to labor relations, as it seems at first glance. The organization is obliged to store it for five years after replacing it with a new one. GENERAL PROVISIONS
The remuneration of employees of the Organization includes:
Downtime due to the fault of the employee is not paid. PAYMENT SYSTEMThe system of remuneration in this Regulation refers to the method of calculating the amount of remuneration payable to Employees for the performance of their labor duties. Direct piecework payFor employees of production units (workshops for product development, for loading metal), a direct piecework wage system has been established, since the results of their work can be quantitatively measured and they are expressed in kind. For the production of each unit of production, specific prices are set. Their size is determined by the order of the General Director for six months. The salary is calculated in the following order: the amount of products of one type or another produced by the employee is multiplied by the prices (set for one unit of production). Then the total amounts for each type of product are summed up. The result obtained is the salary, if the reduction coefficient for marriage, provided for in clause 2.2.2, is not applied to this amount. of this Regulation. If the product manufactured by an employee has a defect in the amount exceeding 2% of the total volume of products produced by this employee, a reduction factor of 0.8 is applied to the amount of salary accrued based on the quantity of products produced. For every additional 2% of scrap, the reduction factor is reduced by 0.2. Chord system of remunerationFor brigades and groups working on specific projects and tasks, a piecework remuneration system is established. Employees are paid based on the collective result of the entire brigade (group). 40% of the income received by the brigade goes to the salaries of its employees. The amount received is distributed among the employees by the foreman (team leader). He can distribute the amount to everyone equally, or differentially, depending on the contribution of a particular employee to the common cause and his compliance with labor discipline. Absenteeism for no reason gives the foreman (team leader) the right to reduce the salary of the offending employee by 15%, for appearing at work in a state of intoxication - by 10%. The salary of the foreman himself or the head of the group exceeds the average salary of his subordinates by 25%. The difference in salaries of employees who are members of the same team (group) cannot be more than 20%. Time-bonus system of remunerationFor other employees of the company, a time-bonus system of remuneration is established.
All employees of the company may also be paid an additional one-time bonus for significant achievements in their work.
The procedure for setting the salary of an employeeThe salary (official salary) in this Regulation is understood as a fixed amount of remuneration of the Employee for the fulfillment of labor norms or labor duties of a certain complexity per month. The amount of the salary (official salary) of the Employee is established in the employment contract. The amount of salary (official salary) (excluding additional payments, allowances, bonuses and other incentive payments) of an employee who has fully worked out the norm of working hours cannot be lower than the minimum wage established by federal law. Changing the salary of an employee An employee's salary increases when he is transferred to another position, which implies greater responsibility, workload and, accordingly, higher pay (included in the grade, for which higher wages are provided). The salary can also be increased if the employee consistently shows high results for one and a half to two years, does not violate labor discipline, fulfills and exceeds the plan, demonstrates loyalty to the company and an interest in improving labor efficiency. The decision to raise the employee is made by the head of the employee, draws up a presentation on him and transfers to the personnel service. She considers the submission and, in agreement with the company's management, makes a decision based on the financial capabilities of the organization. An employee's salary can be reduced if, for health reasons or at his own request, he is transferred to a position with less responsibility and load, as well as with less pay. The organization has the right to reduce the salary of an employee if the certification showed that he demonstrates poor work results, does not fulfill the plan, does not cope with official duties, does not have the necessary knowledge in full and the necessary competencies, does not correspond to his position. The decision to reduce the salary can be made in this case only based on the results of personnel assessment and only by a special labor commission, which includes representatives of the personnel service, the head of the company or deputy, the immediate supervisor of the employee, specialists from the legal and financial services. That the labor commission has adopted the decision to reduce the official salary based on the results of certification, the employee is informed at least two months in advance. SUPPLEMENTSTypes and amount of surchargesEmployees of the Organization are entitled to the following additional payments:
Overtime payIn this Regulation, overtime is understood as work performed by the Employee on the initiative of the Employer outside the established working hours, daily work (shift), with the summarized accounting of working time - in excess of the normal number of working hours for the accounting period. For overtime work, the Employees are given additional payments: for the first two hours of overtime work - in the amount of 150 percent of the hourly rate; for subsequent hours of overtime work - in the amount of 200 percent of the hourly rate. These additional payments are not made to Employees who have an irregular working day. Extra pay for work on weekends and holidaysFor work on weekends and holidays Employees with time wages are subject to additional payments:
Extra pay for night workFor the purposes of this Regulation, night work means work from 10 p.m. to 6 a.m. For work in the night shift Employees with time wages are provided with additional payments in the amount of 40 percent of the hourly rate. Additional payments for performing the duties of a temporarily absent Employee For the performance of the duties of a temporarily absent Employee, an additional payment in the amount of 50 percent of the salary (official salary) for the main job is established. The specified additional payment is paid during the entire period of fulfillment of the duties of the temporarily absent Employee. Additional payments for combining professions (positions)For combining professions (positions), an additional payment is established in the amount of 50 percent of the salary (official salary) for the main job. The specified additional payment is paid during the entire period of combining professions (positions). The procedure for calculating and paying surcharges
Types of allowancesThe employees of the Organization are provided with the following types of salary increments:
For a long period of service, the Employee is given a bonus to the salary (official salary) in the amount of 10 percent of the salary (official salary). In these Regulations, long-term work experience is considered to be work in the Organization for more than 10 years. Bonus for intensity, labor intensityFor the intensity, intensity of work, the Employee is given a bonus in the amount of up to 20 percent of the salary (official salary). Specific amounts of allowances are established by order (instruction) of the head of the Organization. Allowance for the use of a foreign language in workFor the use of a foreign language in the work of the Employee, an allowance is set in the amount of 15 percent of the salary (official salary). The specified allowance is established for Employees whose job duties include contacts with foreign partners or work with foreign literature. Drivers allowanceDrivers of the Organization are given a premium for classiness in the amount of up to 10 percent of their official salary. The specific amount of the allowance is established by order (instruction) of the head of the Organization. BONUSTypes of bonusesEmployees of the Organization holding full-time positions are given current and one-time (one-time) bonuses.
Bonuses are not accrued to Employees who have disciplinary sanctions for:
The specified order is made out by the order of the head of the Organization. Rewarding the leaders of the organizationAwards to the CEO, Executive Director, Advisor to the CEO, Business Development Consultant.
MATERIAL AID
The employer may recognize other circumstances as extraordinary.
CALCULATION AND PAYMENT OF SALARY
In case of failure to perform official duties for reasons beyond the control of the parties to the employment contract, the Employee retains at least two-thirds of the salary (official salary). In case of failure to perform official duties due to the fault of the Employee, payment of salary (official salary) is made in accordance with the amount of work performed. Downtime due to the fault of the Employer, if the Employee warned the Employer in writing about the beginning of downtime, is paid in the amount of at least two thirds of the average salary of the Employee. Downtime for reasons beyond the control of the parties to the employment contract, if the Employee warned the Employer in writing about the start of downtime, is paid in the amount of at least two-thirds of the salary (official salary). Downtime due to the fault of the Employee is not paid.
In the event of a dispute over the amounts due to the Employee upon dismissal, the Employee shall be paid an amount not disputed by the Employer within the period specified above. In the event of the death of the Employee, wages not received by him are issued to members of his family or a person who was dependent on the deceased, no later than one week from the date of submission of documents certifying the death of the Employee to the Organization. WAGE INDEXATION
EMPLOYER'S RESPONSIBILITY
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation does not oblige the employer to draw up a Regulation on remuneration. Nevertheless, it is more convenient for large organizations with a complex system of payments to have a separate document that will combine all the information about the structure of remuneration, dates and procedures for issuing salaries, etc. Some companies go further - they put everything related to bonuses into another local act. However, this is also optional. Why are these provisions needed when the Labor Code of the Russian Federation obliges to indicate the procedure for remuneration in the Internal Labor Regulations (Art. Labor Code of the Russian Federation) and the Labor Contract (Art. Labor Code of the Russian Federation)? When making decisions to draw up / not draw up a Regulation on remuneration, the employer must remember that any change in the employee's salary must be reflected in his employment contract. This means that the organization is obliged to conclude an additional agreement to the employment contract with each employee who will be affected by the change. If a separate document is approved, then the salary and compensation parts can be indicated in the employment contract, and for incentive (bonus) payments, make a reference to the Regulation, for example: “Bonuses are paid in accordance with the Regulations on remuneration of employees / Regulations on bonuses”. And all the adjustments will go through the new editions of the document. A detailed payment scheme "weights" the employment contract, makes the document cumbersome. It is advisable to approve the Regulation on remuneration if, in addition to salaries, employees in the organization receive any additional payments, compensations, or if different remuneration systems have been adopted for different categories of employees. In addition, the Regulation on the remuneration of employees insures the organization against the tax: the document justifies the legitimacy of attributing certain costs to the wage fund, thereby reducing the income tax base. Amounts not included in the Regulations on remuneration, the employment contract and / or the Internal Labor Regulations may be challenged by the tax inspectorate. There is one more argument - the employer is obliged, when paying salaries, to give the employee a notice (pay slip) with a detailed description of all accruals and deductions (Art. Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The organization develops the notification form independently and approves the Regulations on remuneration. How to draw up a Regulation on the remuneration of employees?The content and structure of the Regulations on the remuneration of employees are not strictly regulated by the current legislation. The employer should focus primarily on the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, as well as existing regional and industry agreements that regulate all kinds of allowances and surcharges. An important document is the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation. It reflects the regional coefficients, which the employer is obliged to say in local regulations. The main requirement for the Regulation on remuneration is that the document should not worsen the position of the employee in relation to labor law. The structure of the Regulations may include the following sections:
This is an approximate list of sections that may be in the Regulations. At its discretion, the employer may separate into a separate part the procedure and terms for the payment of wages, the general scheme of remuneration, or deductions from wages accepted in the organization. Who approves the Payment Policy?Depending on the state of the organization, accountants, specialists from the economic department, legal service, documentary and legal support, etc., may participate in the development of the Regulations. If the enterprise has a trade union organization or a representative body of workers ( Art. Labor Code of the Russian Federation), the draft Regulation is necessarily consistent with them. If there is no elected body, the head approves the project solely by his order. A significant point: the employer must familiarize employees with the Regulations on remuneration (including the new version of the Regulations) at least two months before the document enters into force. That is, in the order by which the head approves the Regulation, the date of entry into force of the document should be indicated - not less than two months later. All employees of the organization are required to familiarize themselves with the Regulations on remuneration when hiring or two months before the new edition is put into effect. Notifications are issued individually to each, in paper form. Employees can leave signatures on reading the Regulations on the notifications themselves, in a special journal or on familiarization sheets. Violation of these terms can become a reason for labor disputes and entail administrative liability. |
Popular:
New
- How to get to the business lounge at the airport
- Irrevocable ICPO IRREVOCABLE CORPORATE PURCHASE ORDER (ICPO)
- Types of value of appraisal objects
- Basics of metalwork assembly work
- Fitting and assembly work
- Test: Object, subject, basic concepts and tasks of logistics
- Practical recommendations for establishing ranges of value obtained by various approaches or methods - Association "Self-Regulatory Organization of Appraisers" Expert Council Me
- Formation of the market of science-intensive products and services
- Unified Tariff and Qualification Directory
- Purchases abroad, import, overseas online purchases and parcels



 The position is classified as internal normative-administrative act regulating one of the main activities of the organization.
The position is classified as internal normative-administrative act regulating one of the main activities of the organization. This provision should be developed taking into account the specifics of the conditions of labor production activities, the procedure and methods for paying material accruals to employees.
This provision should be developed taking into account the specifics of the conditions of labor production activities, the procedure and methods for paying material accruals to employees. All items relating to bonuses and remuneration of employees must have legal background- with a detailed description of the accrual process and links to regulatory and legal state acts on the basis of which payments were made.
All items relating to bonuses and remuneration of employees must have legal background- with a detailed description of the accrual process and links to regulatory and legal state acts on the basis of which payments were made. The document considered in this article can be accepted once and not have time limits on the validity period. labor law in this regard. no specific periods. However, in some cases, the need for revision still arises.
The document considered in this article can be accepted once and not have time limits on the validity period. labor law in this regard. no specific periods. However, in some cases, the need for revision still arises.