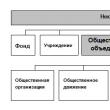
Sections of the site
Editor's Choice:
- Earnings on binary options from scratch
- How to make money on binary options for a beginner
- How to make money by viewing ads
- How can you earn on maternity leave without investing personal funds?
- How to open an IP: step by step instructions
- Implementation of KTU: how to calculate the effectiveness of each employee
- Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation At an enterprise with 6,000 employees
- Personnel of the organization and labor productivity
- The rhythm of production
- Theoretical foundations of the organization of production
Advertising
| The objectives of the financial management of the organization. The structure of the financial and economic service The financial department consists of |
|
This Regulation on the Financial Department discloses the main functions and tasks of the financial department, as well as the rights and obligations of the financial department. REGULATIONS ON THE FINANCIAL DEPARTMENT (ABOUT THE FINANCIAL AND ECONOMIC DEPARTMENT)1. General Provisions Recommended to visit financial seminars for economists and financiers. Schedule for this quarter >>> 1.1. This Regulation on the Financial Department (hereinafter referred to as the Department) of the Financial Department (hereinafter referred to as the Department) is an internal document of the Company that determines the legal status, tasks and functions, structure and formation procedure, rights and responsibilities of the Financial Department. 1.2. The Financial Department is a structural subdivision of the Department and reports to the Head of the Financial Department, as well as the Financial Director of the Company in accordance with the organizational structure of the Company and the order of the General Director of the Company on the distribution of powers and responsibilities. 1.3. The Finance Department in its activities is guided by the legislation of the Russian Federation, the Charter of the Company, decisions of the Board of Directors of the Company, internal documents of the Company, instructions of the Head of the Financial Department, Financial Director and these Regulations. 1.4. The Financial Department interacts with the structural divisions of the Company in the manner determined by the internal documents of the Company. 2. Main tasks of the Finance Department 2.1. Implementation of the financial strategy and financial policy of the Company; 2.2. Organization of the financial activities of the Company for the purpose of efficient use of financial resources; 2.3. Development of forecasts for the economic development of the Company and participation in the formation of key performance indicators. 2.4. Participation in the development of business plans, drawing up long-term and current financial plans and budgets of the Company and operational control of their implementation; 2.5. Providing the necessary financial operational, regular and analytical information to internal and external users; 2.6. Comprehensive economic and financial analysis of the Company's activities, development of measures to improve the efficiency of financial management, reduce financial risks and increase the profitability of the Company; 2.7. Control over compliance with financial discipline, timely and complete fulfillment of contractual obligations, expenses and income; 2.8. Interaction with counterparties and financial institutions within the competence. 3. Main Functions of the Finance Department The purpose of financial work is to organize the circulation of capital with financial resources and distribute them in an optimal way over different stages of the circulation. The listed tasks have specific implementation mechanisms, their own rules and techniques, far from the rules and techniques of accounting. Although financial work is regulated by state-level regulations, the financial manager is more free in making management decisions. Therefore, the following provisions are included in the responsibilities of the financial department: ѕ drawing up tactical and operational plans for financing; ѕ calculation and adjustment of the norms of working capital for individual items, elements, types of reserves and costs in general for the organization; - identification of sources of financing, determination of volumes and sources of investments, formation of reserve funds and financial reserves of the enterprise; ѕ consideration of prices for products manufactured by the organization, control over the use of funds, funds and reserves, the formation of financial and economic calculations, participation in the preparation of draft contracts, justification of forms of payment. The financial department in its activities is closely connected with the economic, supply and marketing, technical and production services of the enterprise and, together with other departments, provides: ¾ with the marketing service and the sales department - drawing up planning documentation for the supply of finished products, developing prices, payment terms; ѕ with the supply service - development of prices and delivery schedules, determination of the optimal order size and stocks, control over stocks of inventory items; ѕ with the department of capital construction - development of title lists of buildings and facilities, plans for financing capital investments by the production services of the enterprise - participation in the development of norms, standards and limits for the consumption of production resources, control over the remains of work in progress; * with design and technological services - participation in the preparation of plans for research and development work, organization of funding; ѕ with accounting - checking the correctness of the preparation of estimated and financial estimates, these audits and inventories. Organization of financial workFormation of financial work in an organization - in market conditions, the formation of correct work includes the goal of timely fulfilling obligations to budgets, own employees at the enterprise, other business entities, the credit system, as well as effective financial management - management. The organization of financial work at an enterprise involves optimizing the management of cash flows that arise in the course of financial and economic activities, maximizing profits and improving the welfare of the owners of the enterprise. Financial work at the enterprise, as a rule, is allocated to an independent service, its size is determined by the scale of activity and industry characteristics. For example, at large enterprises, in holdings, financial directorates or financial organizations are created as independent structural units. The head of the financial service reports directly to the general director (director) of the organization and together with him is responsible for the financial condition of the commercial organization. Usually, the financial director of a large enterprise has several functional financial works under his command, that is, structures (links): cash flow management, financial planning, raising borrowed funds and issuing securities, investing, risk management and insurance. The organization of financial work in a medium-sized enterprise is concentrated in the financial department or is entrusted to a specialist in the field of financial management - a financial manager who is part of the functional economic unit. Financial work can also be performed by financial sectors as part of the planning and financial, financial and marketing, financial and accounting or other divisions of the enterprise. Functional structures for managing financial work in small enterprises, as a rule, are not created. Due to the insignificant volume of organization of financial work at the enterprise, the obligations for its execution are usually assigned to the owner of the enterprise, its director or accountant. Regardless of the scale of activity, the peculiarities of financial management at the enterprise, such work includes three areas: financial planning, operational work and control and analytical work. In its course, the following main tasks are solved: * providing the necessary financial resources to replenish production and social development; ѕ solution of problems to increase profits and increase profitability; ѕ ensuring the fulfillment of one's own obligations to the budgets, employees of the enterprise (in terms of wages), suppliers, banks, etc.; * determination of ways of efficient use of property, fixed assets and working capital; ѕ managing investment activities and achieving maximum financial performance; ѕ organization of control over financial decisions, rational use of financial resources, safety of working capital. The organization of financial management at the enterprise helps the company survive in a competitive environment, ensure a stable financial position, maximize the "price" of the enterprise, profits, minimize costs, profitability, increase production and sales. The enterprise has the right to increase its own income through its core activities and be active in the stock market (securities market), take part in the activities of other enterprises and organizations, develop related areas of activity, use other financial work of the enterprise, where there is no contradiction to the law, all this is necessary in order to increase the overall financial result. The main functions of the finance department are to find inefficient processes and develop ideas to increase profits. Read what other tasks the financial service solves, what divisions it includes, and also download the regulations on the financial department. The finance department can be compared to an oracle. The top manager asks questions:
Download and get to work: How to calculate the optimal number of financial service employeesIf there are too few employees in the financial department, they cannot cope with the volume of work. A lot of them are idle and eat up the company's money. To avoid such problems, determine the optimal number of subordinates. Functions and tasks of the financial departmentTo determine how many specialists should work in the financial department of the enterprise, and what kind of specialists they should be, the scheme of functions and objects of the financial department will help.
The list of functions and objects is so extensive that at first glance, it seems that a third of the staff list should be given to the financial service. But it's not. We will consider each object and functions in sequence and determine which employee should perform them. The first block of company financeIncome and expensesFinancial Controller. The person who starts the finance department. The one who is first hired in the financial service, and as it grows, he often becomes a financial director. In small companies, the financial controller often creates management accounting from scratch, develops documents, analytics and processes for which accounting should be kept. In medium-sized companies, financial controllers are actively involved in the further improvement of management accounting, and daily routine tasks are performed by financial analysts subordinate to them. In large companies, financial controllers and financial analysts work in dedicated divisions - financial control departments by areas of activity (by product, region, type of expense, etc.), where they are engaged in planning, accounting and analysis within their area. Sometimes it becomes necessary to bring planning into a separate function and create a planning department, or a budgeting department. PricePricing functions are not too different from revenue and expense calculations. Therefore, they are performed either by the same financial controllers, if the enterprise is small, or by the Pricing Departments. All pricing and pricing policy management activities are carried out jointly with the Commercial Department, because financiers can give only one of the components of the price - cost and profit, the second component - the market, is not in their competence Reporting (local, IFRS)Maintaining local reporting, of course, is the responsibility of the accounting department. Whereas reporting under IFRS often handled by a financial controller, an IFRS specialist, or entire departments of IFRS. If for one reason or another an enterprise needs a planned reporting package, then specialists from the financial control department can also make it on the basis of the BDR, BDDS and the investment budget. An internal audit of local financial statements can be a task for the financial controller. Or create an internal audit department. It all depends on scale, of course. External audits are usually carried out by a strong alliance between the chief accountant and the financial control department. The analysis of key financial indicators and the writing of analytical notes are usually carried out by the same financial controllers. Management reportingManagement reporting is the responsibility of the financial department. Accordingly, the full cycle from planning to analyzing the results obtained lies with the financial controllers. Or, in the presence of a dedicated unit, on employees of the Management Reporting Department. The second block of company financesCashIf in the calculation of income and expenses the financial controller was the main one, then in the management of funds the key figure is the treasurer. Short-term planning tools DS - payment calendar, and medium-term - the cash flow budget is in the area of his responsibility. On a daily basis, he coordinates requests for payment and forms registers of payments, monitors the profitable placement of DS on time deposits. In small companies, the same financial controller can be the treasurer. But such a combination is effective only if the company conducts no more than 30 operations daily and it has well-automated business processes in finance. The union of the treasurer and accountant works well in the payment area for medium-sized enterprises, and for large enterprises it is necessary to create a treasury department. Working capitalWorking capital management is a related field to cash management, so the treasurer also handles it. With large companies, it is advisable to allocate the functions of controlling accounts receivable to a special department. Additional and related featurestaxesThe functions of the financial control department may include reducing the tax burden by developing methods for optimizing and planning tax schemes. In fact, this is a related function of the chief accountant, but it all depends on the distribution of responsibilities in the enterprise. In large holdings, it is advisable to create a position of a tax consultant or a tax department. TreatiesIn business sectors based on contracting with buyers and suppliers, it is essential to establish control of financial specialists over newly entered into contracts. On the one hand, this will reduce the number of financial errors when concluding a contract, such as:
On the other hand, this will allow financiers to include new contracts in planning, remove key data from them, and maintain a portfolio of contracts. Capital investmentsAt a certain stage of development, it becomes obvious for an enterprise that fixed assets need to be managed especially carefully, because their cost is huge. And with the help of competent management, you can save a significant amount on payments, taxes and free up cash for working capital. Capital investment management is also handled by the financial control department or a dedicated unit. Financial investmentsWhen an enterprise has free cash or retained earnings that can generate additional income, the task of the financier becomes their profitable investment. In small volumes, the financial director is pitted with the management of financial investments. And when the volumes grow, it is advisable to allocate an Investment Analyst under the management or create an investment department Business processesIn process-oriented companies, the question is always acute: “Who will participate in the development of processes from the company?” Due to their mindset, financiers are usually good at this and are willing to be included in various project teams. In addition, the financiers on duty must be aware of the basic business processes in order to know where to go for information. KPIA very common practice is to put the finance department in charge of calculating KPIs, especially if the KPIs are not numerous or complex. Otherwise, this is the area of responsibility of a dedicated unit of the KPI department. But the development of KPI should not be completely delegated to financiers, because in the end you will get good KPIs for a stagnant business, but not for rapid development. Structure of the financial departmentThe structure of the financial department depends on the specific task of the company's development. The unit has basic functions (budgeting, management accounting, internal control, financial reporting) and additional ones. The latter may vary depending on the priorities of the current stage of the company's development. Table. An example of the structure and staff of the financial service of an enterprise
We have covered most of the functions of the finance department and we hope that the article will help you create an effective and not bloated department.
Ph.D., Pletnev Yu.M., In modern conditions, more and more significant in their consequences for the activities enterprises decisions become financial managers and analysts. Pricing and dividend policy, capital management are of fundamental importance for the results of its activities. Russian transition economy to market relations raised a large number of questions and presented new requirements for management finance enterprises. Studying the laws of the market and organizing financial relations took place “on the fly”, and the automatic transfer of the concepts of the West to domestic soil led to the rejection of quite viable ideas by Russian practitioners. The above reasons partly influenced the economic condition of Russian enterprises. In this regard, it seems necessary to discuss the problems organizations and functioning financially-economic services enterprises. Undoubtedly, this service should meet his interests, depending on the goals and objectives facing him. We propose to discuss these problems on the example of CJSC Voronezhstalmost, other enterprises of JSC Mostostroyindustriya and some industrial enterprises of the city of Voronezh, which have a single, non-serial nature of production. The article discusses and analyzes organizational structures financially-economic services enterprises, recommendations on the composition of their functions have been developed. A peculiar subject of labor of the financial and economic service is money and cash flows that arise within the enterprise itself and outside it, connecting it with other enterprises, the credit and banking system, business entities that are in the association. To manage the finances of enterprises, a financial mechanism is used - a system for managing financial resources with the aim of effectively influencing the final results of production. The financial mechanism is designed to ensure the implementation of finance functions related to:
The first function implies the optimal security of the enterprise with cash. Cash flow optimization is one of the main tasks of the financial service. The distribution function is associated with the reimbursement of production costs and the formation of income. This income, in turn, is distributed between the enterprise and external organizations with which it is bound by obligations, as well as between the enterprise and the state. The control function involves the use of various indicators and the establishment of economic incentives or sanctions. The main goal of the financial service is the most complete implementation of the functions of finance by strengthening the financial position of the enterprise by increasing its profitability, profit, increasing labor productivity, reducing costs, improving product quality and introducing new advanced technologies and scientific achievements. Among the most important tasks assigned to the financial and economic service, in our opinion, should include:
The organizational structure of the financial service reflects the composition of numerous functional divisions of the enterprise and determines the coordination of their joint activities towards achieving the goals set for the enterprise. It is this coordination that is the basis of the organizational structure, which is usually defined as a set of stable relationships in an organization. Relationships are here treated as expressions of relationships, not as any specific action. Through structural links, coordination relations between the divisions of the enterprise are realized, interaction of functional services is carried out, in which two important components are distinguished: the rights of the structural unit and its information support. Unfortunately, in the economic literature, including in the literature on financial management, not enough attention is paid to the composition, interaction of individual functional units of the financial and economic service of the enterprise. Financial and economic management is part of the process of general enterprise management, therefore, management in this area can be built according to management schemes traditionally attributed to the enterprise as a whole. These can be linear-functional management schemes that have proven themselves in conditions of stability, or flexible and adaptive schemes oriented to changing market conditions, or matrix, product management schemes. The main condition for choosing a control scheme is that it must meet the conditions of production and the type of organization. Let us consider as an example the organizational structure of the financial and economic service at the enterprises of Mostostroyindustriya JSC. On fig. 1 shows the organizational structure of the economic service of Ulan-Udestalmost CJSC. Enterprises in Kurgan and Ulan-Ude were built on the model of the Voronezh plant, repeating its organizational structure. Over time, it began to change in all enterprises. Rice. 1. Organizational structure of the financial and economic service of Ulan-Udestalmost CJSC The organizational structure of the financial and economic service of the Ulan-Ude plant has undergone the least changes to date. This management scheme can be considered the original, preserved from the time of the planned economy. It includes traditional groups that are part of the accounting and economic departments. On fig. Figures 2 and 3 show the schemes of financial and economic services of the Voronezhstalmost and Kurganstalmost enterprises.
Rice. 2. Organizational structure of the financial and economic service of ZAO Voronezhstalmost
Rice. 3. Organizational structure of the financial and economic service of Kurganstalmost CJSC There are many similarities in the organizational structures of the financial and economic services of these enterprises. The highest management level is the CEO. The second level is the Deputy General Director (at the Kurgan enterprise it is traditionally - "for economics and finance", at the Voronezh plant - "for long-term development"). At the same time, the chief accountant and his department, according to the schemes of the organizational structure, report directly to the director. To a greater extent, this is appropriate for the Voronezh enterprise, since the main activity of the deputy director is related to long-term planning, work with customers and justification of product prices. The same functions are typical for the Deputy Director for Economics and Finance of the plant in Kurgan. It is in his subordination that the department of foreign economic relations is located, the work of which is primarily aimed at providing production with orders. The subordination of the chief accountant and his department directly to the general director is explained by the correspondence of the organizational structure to the essence of the planned economy, as well as the right of the chief accountant to manage funds in the current account based on the requirement of a second signature on payment documents. The personal responsibility of the chief accountant for the use of funds is also retained. To date, the subordination of the chief accountant directly to the general director is enshrined in the statutory and official documents of enterprises. One of the elements of the organizational structure of the Kurgan plant deserves special attention - the subordination of the legal department to the deputy director for economics. The work of this service is largely connected with the preparation of contracts with external organizations, with the assessment of the legality of decisions taken by economic services, with the fulfillment of the obligations of the enterprise to the state and contractors. Therefore, such a position of the legal service in the organizational structure, in our opinion, is natural. Also, in our opinion, the direct subordination of the department of foreign economic relations (OVES) to the deputy director for economics of the Kurgan plant or the deputy director for the prospective development of the Voronezh plant is completely justified. The main activity of OVES is aimed at providing production with orders, which is closely related to the economic analysis of a potential order. It is inexpedient and expensive to have a group of economists both in the planning department and in the OVES. Consolidation of these services under the leadership of the Deputy Director is quite justified. Evidence confirming the expediency of the provisions of the OVES and the planning and economic service are the changes in the organizational structure of the Voronezh plant over the past few years. After the creation of the foreign economic relations service at the plant, the price bureau, responsible for the calculation of products and subordinate to the chief economist, was transferred to the structure of the foreign relations department. Later, he was again returned to the direct subordination of the chief economist. At present, the organizational structure looks more complete: both economists and marketing specialists are united under a single leadership (at the Voronezh plant - the deputy director for long-term planning, in Kurgan - the deputy director for economics and finance). The Bureau of Prices remains under the jurisdiction of the Chief Economist, works in the structure of the Financial and Economic Service and ultimately reports to the Deputy Director for Economic Affairs. As part of the economic services of the plants there is a department of labor and wages (OTiZ), which is traditional for the structure of the financial and economic service. A feature of the structure of the economic service of the Kurgan plant is the allocation of an independent financial department in its composition. His position and subordination directly to the Deputy Director for Economics and Finance meets modern requirements. The Voronezh plant does not have an independent financial department. Its functions are performed by the financial group as part of the accounting department. There is no doubt that the role of the financial service has increased and is intensifying with the development of market relations in Russia. Currently, financial departments are needed, which are charged with the task of forming a rational capital structure, assessing the availability of working capital for an enterprise, managing cash flows, conducting financial analysis, searching for sources of financing, budgeting, etc. In this regard, the experience of the Kurgan plant in dividing accounting functions and the financial department seems to meet the requirements of the times. At the Voronezh plant, the financial group is part of the accounting department. In this regard, the main functional responsibilities of accounting include: financial management, accounting for materials and other property, depreciation, financial reporting and taxes. At the same time, there is no analytical service in the accounting department that would assess the current financial and economic state of the enterprise, sources of financing, and investment flows. There is no such service in the structure of the planning and economic department. The calculation of the cost of new orders, the comparison of planned and actual indicators are carried out by the economic service, financial activity is controlled by the accounting department, which ascertains the movement of financial resources, manages them and sums up. Thus, there is no forecasting of the financial and economic state of the enterprise, an operational analysis of its production activities. The assessment of the economic condition is carried out on the basis of actual data, when it is no longer possible to influence them. In order to improve the organization of work and coordinate the activities of the financial and economic service, each of the analyzed enterprises can and should optimize the organizational structure of this service. It is no coincidence that the size of the accounting department has grown significantly at the Voronezh plant in recent years. An increase in the number of functional responsibilities within one department negatively affects the results and efficiency of its work. To change the situation, it is necessary to streamline and clearly delineate the functional tasks of the financial and economic service and reflect this in its organizational structure. Today, it is important, in our opinion, to include in the financial and economic service the positions of specialists in financial planning, conducting current operational analysis, assessing the attractiveness of investment projects, compiling an enterprise's budget, evaluating various sources of financing, i.e. positions of financiers or financial managers. Along with the enterprises of JSC Mostostroyindustriya, the organizational structures of other enterprises of Voronezh were analyzed: OJSC Rudgormash and the Voronezh Carriage Repair Plant named after Telman (VVRZ). Schemes of organizational structures of economic services of these enterprises are given below in fig. 4 and 5.
Rice. 4. Organizational structure of the financial and economic service of JSC "Rudgormash" It should be noted that if the first three enterprises are commensurate in terms of production volumes, then the Rudgormash plant and VVRZ are almost twice as large both in terms of production capacity and the number of employees. The structure of the financial and economic service of the Rudgormash enterprise is focused on modern requirements for managing the finances of a commercial organization and, in our opinion, is quite complex. The entire service is headed by the Deputy Director for Economics and is divided into departments: economic planning and accounting and analysis (which includes accounting and financial departments). The service also includes a department of taxation. The planning and economic management includes traditional divisions: economic, organization of labor and wages. The accounting and finance management structure includes services that meet modern requirements. Here, in addition to the traditional sectors, separate services are distinguished in the accounting department: management accounting and analysis, budgeting, mutual settlements and work with banks. However, the subordination of the financial department to the chief accountant seems unjustified. The head of the financial department has no direct access to the head of the economic service. It is more expedient, in our opinion, to leave for each of the services only their inherent functions and bring each of them to direct subordination to the deputy director for economics: accounting, planning and economic and financial departments. The tax department is removed from the accounting department, although it builds its activities on the basis of accounting data and, therefore, should be part of the accounting department. The organizational structure of the economic service of the VVRZ named after Telman, on the contrary, is not complicated by the modern division of functions and is similar to the organizational structure of CJSC Ulan-Udestalmost. The difference between the financial and economic service of the Telman plant is that it is headed by the deputy director for economics. The service itself is divided into the economic department and accounting. Each of the divisions includes traditional functional groups and bureaus. It is worth paying attention to the fact that the economic department of this enterprise has a sector of accounting and analysis. Typically, such a sector is present in the accounting structure (in its financial part).
Rice. 5. From conversations with heads of economic services, it seems that practical economists see the analytical group either in the financial or economic departments, least of all linking its activities with purely accounting departments of accounting. The same opinion about the position of this group in the organizational structure is shared by the authors of the work. At the time of the survey of the activities of the financial and economic service of VVRZ, an additional specialist in taxation was introduced into the accounting department. In our opinion, in the current situation, the presence of such specialists as part of the economic service of the enterprise has become a necessity. From the analysis of the considered organizational structures of financial and economic services, the identified patterns of their change and the requirements for them, we can draw conclusions about the conditions that the financial management scheme should meet at an enterprise with a nature of production similar to production at the enterprises of Mostostroyindustriya JSC:
The main role in the process of managing the finances of an enterprise is assigned to the deputy director for economics and finance (in other words: director of economics, vice president of the company for finance), who is directly subordinate to the general director. This is a key figure responsible for the development of strategies and tactics of financial management, their implementation to achieve the goals of the enterprise. The duties of the Deputy Director for Economics and Finance include solving problems that determine the financial policy and implement the economic goals of the enterprise. Let's name some of them: the choice of service management schemes, ways and means of their improvement, organization of the effective work of the economic service, selection and placement of personnel, management of structural divisions of the service, provision of financial and economic indicators of the enterprise to interested parties, work with the banking system and business partners , formation and development of relations with the owners. The next level of management of the financial and economic service is the chief specialists and heads of departments who head the functional services under the direct supervision of the deputy director for economics and finance. This is the accounting department headed by the chief accountant; financial department headed by the head of the department; the planning and economic department, the department of labor and wages and the price bureau under the unified leadership of the chief economist. The organizational structure of financial management, which allows optimizing financial flows arising from the production and financial activities of an enterprise, may look like a diagram shown in Fig. 6. In the proposed structure, the accounting department is mainly responsible for the choice of accounting policies and the organization of accounting activities. She is also responsible for the reliable reflection of business transactions in the accounting, the provision of accounting data to internal and external users, the correctness of tax accounting. In addition to traditional functional units, its structure may include sectors of internal audit, management and tax accounting. The tax service is part of the accounting department for the following reasons: firstly, due to the fact that all forms of financial reporting - balance sheet, income statement, cash flow statement, etc. - are formed in the accounting department. Secondly, by the nature of its activities, the tax service is an accounting unit. Thirdly, rational restrictions on the number of individual units in the economic service are necessary. The accounting department also collects information on costs and posting them by type for further presentation in the format of "fixed - variable costs" within the framework of management accounting. Cost differentiation is important for conducting operational analysis, calculating the "break-even point". The location of such an analysis should be noted. Traditionally, it is referred to as management accounting, which is a part of accounting activities. In practice, the conduct of operational analysis is more often attributed to the functions of economists-analysts, linking it with the activities of the financial or economic planning department. It can be noted that the analysis of "costs - volume - profit" is an integral part of financial management, therefore, in the presented organizational structure, cost accounting should be singled out as a function of accounting, and the analysis should be assigned to the analysts of the economic service. In our opinion, this approach to the division of functions seems to be more correct, since the planning of production activity indicators, the comparison of their planned and actual values should be carried out by one service.
Rice. 6. In the recommended organizational structure, the financial service, headed by the head of the department, is separated into a separate structural unit. The financial department is directly subordinate to the Deputy Director for Economics and Finance. This position of the department is dictated by the requirements that are placed on this service by the modern nature of economic relations. In a market economy, the tasks solved by the financial department are of high importance for the enterprise. The competence of the department includes: searching for sources of financing for production, managing the capital structure of an enterprise, assessing the availability and sufficiency of working capital, tracking revenue, managing accounts receivable and payable, analyzing the compliance of the company’s funds with its financial obligations, financial planning and forecasting, attracting and control briefly The economic service, headed by the chief economist, includes a planning and economic department and a department for the organization of labor and wages. The activities of the planning department are related to the solution of the following tasks: planning of production activities and related costs, analysis of actual data on the volume and costs of production, identification and analysis of the causes of deviations from planned indicators and standards. This service develops ways and methods to reduce costs, prepares pricing decisions for various types of products, together with other structural divisions is the developer of business plans for the enterprise, collects and maintains reporting documents on its production activities, determines and monitors profits received from production and sales products. Planned and actual profit is the object of close attention of the planning department. This implies the expediency of conducting an analysis of the current economic state of the enterprise in this particular department. The service in which plans were developed and the actual results of production activities were monitored should be the place for conducting operational analysis, analytical work to evaluate the final indicators in comparison with the planned ones. In direct connection with the planning department is the department of organization of labor and wages. Its functional purpose is the organization, regulation and accounting of labor costs in the enterprise. The department conducts justification of prices for production operations, takes into account and analyzes labor costs. Of course, the economic service is not able to separately carry out production planning or prepare reports. In this work, communication with production departments, marketing and technical services of the enterprise is important. In the process of preparing reports and conducting analysis, economists need to interact with the accounting department and the financial department, as well as the sales department. As noted in the analysis of the organizational structures of enterprises included in Mostostroyindustriya JSC, it is advisable to introduce a department of foreign economic relations and a legal service into their economic services. This proposal was reflected in the organizational structure, which is recommended for implementation in ZAO Voronezhstalmost (Fig. 7).
The activities of the OVES are related to the economic feasibility of projects that are supposed to be put into production. In our opinion, having an economic analysis group in the OVES is prohibitively expensive for such enterprises. The inclusion of OVES in the structure of the economic service, as it was done in Kurgan, is, in our opinion, a good decision. A similar situation exists with the legal service. Its activity is closely connected with the work of economic structures. The association of OVES, legal service and economic structures under the control of the Deputy Director for Economics and Finance seems to be rational from the point of view of coordinating their joint activities. The recommended organizational structure of the financial and economic service, in our opinion, most fully reflects the requirements for this service. However, it is indicative. It can be adjusted depending on the company. With a particular situational approach to building an organizational structure, it is important to maintain functionality, that is, the ability to effectively manage financial and economic activities. At large-scale enterprises, the service may contain a large number of groups, bureaus, departments. A small enterprise may have a service where the functions and responsibilities of sectors or groups can be combined and carried out by a smaller number. Literature
Also on this topic. Added to site: 1. General Provisions1.1. The financial department, being an independent structural subdivision of the enterprise, is created and liquidated by order of [name of the position of the head of the enterprise]. 1.2. The department reports directly to [name of the position of the head of the enterprise, commercial director]. 1.3. The department is headed by a chief appointed to the position by order of [name of the position of the head of the enterprise]. 1.4. The head of the finance department has [insert as appropriate] deputy(s). The duties of the deputy(s) are determined by the head of the finance department. 1.5. Deputy(s) and heads of structural units (bureaus, sectors, etc.) in the financial department, other employees of the department are appointed to positions and dismissed from positions by order of [name of the position of the head of the enterprise] on the proposal of the head of the financial department. 1.6. In its activities, the department is guided by: the Charter of the enterprise; By this provision; Legislation of the Russian Federation; 1.7. [Enter as required]. 2. Structure2.1. The structure and staffing of the department is approved by the [name of the position of the head of the enterprise], based on the specific conditions and characteristics of the enterprise's activities, on the proposal of the head of the financial department and in agreement with the [HR department, department of organization and remuneration]. 2.2. The financial department may include structural units (services, bureaus, groups, sectors, etc.). For example: a bureau (sector, group) of financial and credit activities, a bureau (sector, group) of financial and investment activities, a bureau (sector, group) of accounting for fixed assets and intangible assets, a bureau (sector, group) of securities, a bureau (sector, group) of methodology and taxation, bureau (sector, group) of operating expenses, bureau (sector, group) of analysis of financial and economic activity, bureau (sector, group) of financial planning. 2.3. Regulations on subdivisions of the financial department (bureaus, sectors, groups, etc.) are approved by the head of the financial department, and the distribution of duties between the employees of the subdivisions is carried out by the [heads of the bureau, sectors, groups; deputy heads of the financial department]. 2.4. [Enter as required]. 3. TasksThe financial department provides the following tasks: 3.1. Organization of the financial activity of the enterprise with the aim of the most efficient use of all types of resources in the process of production and sale of products (works, services) and obtaining maximum profit. 3.2. Implementation of a unified enterprise policy in the field of finance. 3.3. Control over the use of working capital of the enterprise, loans. 3.4. Analysis of the financial and economic state of the enterprise. 3.5. Development of credit policy of the enterprise. 3.6. Development of accounting and tax policies. 3.7. Management of working capital, accounts payable and receivable, as well as costs. 3.8. Ensuring the timeliness of tax payments to the budget, settlements with creditors and suppliers. 3.9. Creation of conditions for the effective use of fixed assets, labor and financial resources of the enterprise. 3.10. [Enter as required]. 4. FunctionsThe following functions are assigned to the financial department: 4.1. Development of the financial strategy of the enterprise and the basis for its financial stability. 4.2. Management of the movement of financial resources of the enterprise and regulation of financial relations arising between business entities in order to most effectively use all types of resources. 4.3. Drafting of long-term and current financial plans with the application of all necessary calculations. 4.4. Preparation of materials for drawing up a business plan for the enterprise. 4.5. Participation in the preparation of draft plans for the sale of products (works, services), capital investments, research and development. 4.6. Development of forecast balances and cash budgets. 4.7. Participation in planning the cost of production and profitability of production. 4.8. Development of profit expectation forecasts, calculation of income tax, preparation of profit distribution plans for the year and quarters. 4.9. Determining the need for own working capital and calculating the norms of working capital, planning measures to accelerate their turnover. 4.10. Work on finding own funds and attracting borrowed funds. 4.11. Determination and implementation of investment policy, participation in the search for additional investment and financial resources. 4.12. Interaction with credit institutions on the provision of credit resources. Preparation and submission of loan applications and quarterly cash plans to banks and credit institutions. 4.13. Organization of work on the conclusion of agreements on the provision of loans. Financial processing of received loans. 4.14. Work on the timely repayment of loans and the return of received credit funds in a timely manner. 4.15. Ensuring the implementation of credit plans, including the payment of interest on the loan. 4.16. Development of a strategy for bringing the company's securities to the stock market with the determination of the costs of using various stock instruments: Determining the type of securities (shares, bills, bonds); Selecting a primary securities dealer or portfolio investor and agreeing with him the terms of sale and the trading platform for primary trading; - [fill in as needed]. 4.17. Work with securities (acquisition of shares, bonds, etc.), control over the portfolio of securities. 4.18. Determining the amount of expenses for the payment of dividends on the company's shares. 4.19. Management of enterprise assets, determination of their optimal structure, preparation of proposals for the replacement and liquidation of assets. 4.20. Determination of sources of financing of capital investments. Development and approval of the capital investment plan. 4.21. Determining the procedure and conditions for financing capital or current repairs of fixed assets, drawing up proposals for attributing expenses to the cost of production. 4.22. Ensuring timely receipt of income. 4.23. Execution of financial settlement and banking operations in a timely manner, including the presentation of payment requests, orders and other settlement documents to banks, receipt of documents for the shipment of products, invoice statements. 4.24. Maintaining operational records of financial, settlement and credit operations performed by the enterprise on accounts in banks and credit institutions. 4.25. Compliance with the cash balance limit set by the servicing bank in the cash desks of the enterprise in accordance with the calculation for setting a cash balance limit for the enterprise and issuing permission to spend cash from the proceeds received by its cash desk. 4.26. Ensuring timely receipt of funds for shipped products (work performed, services rendered), as well as timely payment of invoices from suppliers and contractors for shipped material assets (work performed, services rendered) in accordance with the concluded agreements. 4.27. Organization of work on the transfer of payments and contributions for taxes and fees to the federal budget, the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, the local budget. 4.28. Preparation of necessary materials for mutual offsets. 4.29. Development and implementation of measures that contribute to the timeliness of payments, the choice of forms of settlement with counterparties and ensuring compliance with the rules for conducting settlements. 4.30. Drawing up and submission to the tax authorities of the established documentation on the financial and economic activities of the enterprise. 4.31. Ensuring the timeliness and completeness of the payment of wages to employees of the enterprise. 4.32. Ensuring financing of expenses provided for by financial plans, capital investment plans. 4.33. Participation in the development of proposals aimed at: Ensuring solvency; Prevention of the formation and liquidation of unused inventory items, excess stocks; Increasing the profitability of production; Increasing profit; Reduction of costs for production and sale of products; - [fill in as needed]. 4.34. Implementation of measures to strengthen financial discipline at the enterprise. 4.35. Keeping records of the movement of funds and reporting on the results of financial activities in accordance with the standards of financial accounting and reporting. 4.36. Control over the correctness of the preparation and execution of reporting documentation. 4.37. Ensuring the reliability of financial information. 4.38. Bringing the indicators of financial plans and the tasks arising from it to the structural divisions of the enterprise. 4.39. Implementation of control over the implementation of financial plans by structural units. 4.40. Compilation and submission to the management of the enterprise: Information about the receipt of funds; Reports on the progress of credit and financial plans; Information about the financial condition of the enterprise; - [fill in as needed]. 4.41. Ensuring the implementation of financial, credit and cash plans. 4.42. Identification of possible financial risks, their assessment in relation to each source of funds. 4.43. Development of the enterprise's monetary policy. 4.44. Development of proposals to reduce financial risks and insurance programs. 4.45. Determination of the company's strategy in the field of leasing operations, the implementation of leasing financing. 4.46. Development of measures for the sale, leasing and pledge of part of the assets, liquidation or conservation of individual capacities and facilities (including unprofitable, mobilization). 4.47. Maintaining daily operational accounting of financial plan indicators, including accounting for: Volumes of products sold; Profits from sales; - [fill in as needed]. 4.48. Analysis of the financial and economic activities of the enterprise quarterly and in general for the year. 4.49. Participation in determining the types of products (works, services) that are not in demand on the market, developing programs and measures to stop the production of such products. 4.50. Participation in pricing for certain types of products (works, services). 4.51. Determining the amount of funding for research, development and design and survey work in accordance with estimates and contracts agreed with the structural divisions of the enterprise. 4.52. Coordination of contracts for the performance of research and development work in terms of the reasonableness of the cost of work, as well as compliance with the terms of payment for work. 4.53. Determination of directions and volumes of financing by the enterprise of social programs (children's preschool institutions, educational institutions, charitable events, etc.). 4.54. Control for: Fulfillment of financial plans and budget, product sales plans, credit and cash plans, profit plans and other financial indicators; Termination of production of products that do not have a market; Correct and efficient use of funds; Target use of own and borrowed working capital for structural divisions and for the enterprise as a whole; Compliance with cash discipline; The correctness of the preparation, execution and approval of estimates, calculations of the payback of capital investments; - [fill in as needed]. 4.55. Participation in the determination of financial conditions in the concluded business contracts, examination of draft contracts submitted by counterparties. 4.56. Analysis of the production, economic and financial activities of the enterprise, forecasting the results of the financial and economic activities of the enterprise. 4.57. Analysis of accounting and statistical reporting. 4.58. Providing departments of the enterprise with instructive materials related to the financial activities of the enterprise. 4.59. Development of guidelines on financing operating expenses, capital investments, and other activities. 4.60. Consideration of appeals and letters from citizens and legal entities on issues within the competence of the financial department, organization of inspections, preparation of relevant proposals. 4.61. Participation in holding meetings-seminars with employees of economic, financial and accounting departments. 4.62. Ensuring the protection of information resources (own and received from other organizations) containing restricted access information. 4.63. Formation of complete and reliable information about business processes and financial results of the enterprise, necessary for operational management and management. 4.64. Timely prevention of negative phenomena in the financial and economic activities of the enterprise, identification and mobilization of on-farm reserves. 4.65. Development of measures to ensure the transparency of the financial condition of the enterprise (based on the improvement of management accounting, the transition to international accounting standards). 4.66. Development of draft guidance materials on financing, accounting, reporting and other financial and economic aspects related to the competence of the department, and submitting them for consideration and approval to the relevant structural divisions of the enterprise. 4.67. Participation within its competence in the consideration of issues related to the creation of new enterprises, reorganization and liquidation of structural divisions of the enterprise. 4.68. [Enter as required]. 5. Rights5.1. The financial department has the right: Give instructions within the framework of control over the financial and economic activities of the enterprise on the preparation of financial documentation; Require and receive from other structural divisions of the enterprise the data of the analysis of the economic activity of the enterprise, necessary for the activities of the department; Conduct correspondence on the methodology of financial accounting and reporting, as well as on other issues that are within the competence of the department and do not require agreement with the head of the enterprise; Do not accept for execution and execution documents on operations that are contrary to the law, violate contractual and financial discipline without a corresponding order from the director of the enterprise and the head of the legal department; Represent in the prescribed manner on behalf of the enterprise on issues within the competence of the department in relations with tax, financial authorities, bodies of state non-budgetary funds, banks, credit institutions, other state and municipal organizations, as well as other enterprises, organizations, institutions; Make proposals to the management of the enterprise on bringing the employees of the enterprise to material and disciplinary responsibility based on the results of inspections; Conduct meetings on financial and economic activities of the enterprise; In agreement with [name of the position of the head of the enterprise] Or, as his deputy for commercial matters, involve experts and specialists in the field of financial consulting for consultations, preparation of opinions, recommendations and proposals. 5.2. The head of the financial department approves all documents related to the financial and economic activities of the enterprise (plans, contracts, reports, estimates, certificates, etc.). 5.3. The head of the financial department has the right to sign payment, settlement, credit and other financial documents, make proposals to the personnel department and the management of the enterprise on the movement of management employees, their encouragement for successful work, as well as proposals to impose disciplinary sanctions on employees who violate labor discipline. 5.4. [Enter as required]. 6. Relationships (service relations)Note. This section is given as an indicative one, since over time, official relations between structural and other divisions change (“polished”) and appropriate changes and additions are made to the regulations on divisions. To perform the functions and exercise the rights provided for by this regulation, the financial department interacts: 6.1. With the department of the chief accountant on: Receiving: Lists of creditors and debtors; Accounting information about the activities of the enterprise; Balance and operational summary reports on income and expenditure of funds, on the use of the budget; Reporting cost estimates for products (works, services); Plans for conducting inventories of fixed assets, inventory items and cash; Payroll calculations; - [fill in as needed]. Provisions: Financial, credit and cash plans; Reports on repayment of loans, payment of interest on loans; - [fill in as needed]. 6.2. With the planning and economic department on: Receiving: Medium-term and long-term plans for the production activities of the enterprise; Copies of planned economic tasks of the enterprise divisions; Planned technical and economic standards for material and labor costs; Projects of wholesale and retail prices for the company's products, tariffs for works and services; The results of the economic analysis of all types of activities of the enterprise; - [fill in as needed]. Provisions: Financial and credit plans; Reports on the implementation of financial plans; Financial analysis results; Methodical and instructive materials on the financial activities of the enterprise; - [fill in as needed]. 6.3. With the logistics department on: Receiving: Projects of long-term and current plans for the logistics of the production activities of the enterprise; Reporting data on the movement of material and technical resources, on their balances at the end of the reporting period; Copies of claims filed by contractors; Draft claims against contractors in case of violation of their contractual obligations; Reports on the implementation of logistics plans; - [fill in as needed]. Provisions: Agreed draft claims; Proposals to eliminate the causes that served as the basis for filing claims and sanctions against the enterprise; - [fill in as needed]. 6.4. With the sales department for: Receiving: Draft contracts and agreements for the supply, sale of finished products; Forecasts and plans for the sale of products; Data on the state of stocks of finished products and their compliance with approved standards; Plans and schedules for the shipment of products; Data on the balance of products in warehouses; Proposals for taking measures to reduce excess balances of finished products and accelerate sales operations; - [fill in as needed]. Provisions: financial plans; Information about invoices not paid by counterparties; Information of banks on letters of credit issued by buyers (customers); Notifications on the application of financial sanctions to buyers (customers) who violated their obligations to transfer funds for purchased goods; Approved calculations of working capital norms; - [fill in as needed]. 6.5. With the marketing department for: Receiving: Generalized data on the demand for products manufactured by the enterprise (work performed, services rendered); Marketing plans; Estimated costs for demand formation and sales promotion, advertising campaigns, participation in exhibitions, fairs, sales exhibitions; Information about the competitive environment on pricing policy, turnover volumes, competitiveness, speed of product sales; - [fill in as needed]. Provisions: Agreed cost estimates for demand generation and sales promotion with financial justifications; Analysis of costs incurred per month (quarter, year); - [fill in as needed]. 6.6. With the business department on: Receiving: Plans for current and major repairs of fixed assets of the enterprise (buildings, water supply systems, etc.); Estimated business expenses; Office equipment, forms of documents and stationery necessary for the work of the financial department; Material assets necessary for servicing meetings, conferences, seminars; - [fill in as needed]. Provisions: Agreed cost estimates; Calculations of the payback of capital investments for the introduction of new equipment, means of mechanization; Applications for the necessary inventory and stationery; Reports on the use and safety of equipment and inventory; - [fill in as needed]. 6.7. With the legal department on: Receiving: Decisions on the claims, claims brought by the enterprise; Generalized results of consideration of claims, court and arbitration cases; Explanations of the current legislation and the procedure for its application; Legal assistance in claim work; Agreed materials on the status of receivables and payables, proposals for the enforcement of debts; Analysis of changes and additions to financial, tax, civil legislation; - [fill in as needed]. Provisions: Draft financial contracts for legal expertise; Materials for filing claims, lawsuits in courts; Conclusions on claims and lawsuits brought against the enterprise; Documents on the transfer of funds for the payment of the state duty to satisfy the claims and lawsuits brought against the enterprise; Applications for clarification of the current legislation; - [fill in as needed]. 6.8. From [name of the structural unit] on the following issues: Receiving: - [fill in]; - [fill in as needed]. Provisions: - [fill in]; - [fill in as needed]. 7. Responsibility7.1. Responsibility for the proper and timely performance by the department of the functions provided for by this regulation lies with the head of the financial department. 7.2. The head of the financial department is personally responsible for: Compliance with the legislation of instructions issued by the department, and instructions on the financial activities of the enterprise, financial accounting and reporting; Preparation, approval and submission of reliable consolidated financial statements and compliance with the deadlines for its submission to the relevant divisions of the enterprise, the head of the enterprise, tax, financial and other authorities; Providing the management of the enterprise with information on financial matters; Timely, as well as high-quality execution of documents and instructions of the company's management; Preventing the use of information by employees of the department for non-official purposes; Compliance with the work schedule of the employees of the department. 7.3. The responsibility of employees of the financial department is established by job descriptions. 7.4. [Enter as required]. Head of structural unit [initials, last name] [signature] [day month Year] Agreed: [official with whom the regulation is agreed] [initials, last name] [signature] [day month Year] Head of the legal department [initials, last name] [signature] [day month Year] |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Read: |
|---|
New
- Wage formation factors
- Ultrasonic parts cleaning and degreasing - RUSDORF
- Breeding worms and obtaining biohumus
- Thesis: Profitability of the banking business: assessment and management
- Using reporting for risk analysis and assessment
- Inside view: a day in the life of a criminal investigation officer
- What happy and successful people always ignore
- Do you need to be happy all the time?
- All unhappy people are unhappy for one reason Feelings of happiness and joy in words
- Voronezh ufologist has published a book with personal photos of anomalous phenomena