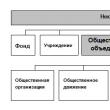
Sections of the site
Editor's Choice:
- Earnings on binary options from scratch
- How to make money on binary options for a beginner
- How to make money by viewing ads
- How can you earn on maternity leave without investing personal funds?
- How to open an IP: step by step instructions
- Implementation of KTU: how to calculate the effectiveness of each employee
- Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation At an enterprise with 6,000 employees
- Personnel of the organization and labor productivity
- The rhythm of production
- Theoretical foundations of the organization of production
Advertising
| Types of temples in ancient Greece and the order system. Presentation on MHK order system of ancient Greece Order of the system of other Greece presentation |
  The famous symbol of ancient Greece Acropolis built by the genius Phidias on a high hill in Athens.   Acropolis in Greek means "Upper City". In ancient times, the Acropolis in Greece served the same purpose as the Kremlin in Rus': in a fenced area were the main shrines and treasures, the treasury of the state, Those who ruled the city were also located here. The acropolis consisted of several magnificent buildings. It was placed on a hill, as if specially created by nature - a steep hill with a flat top.  Citizens who rise here on the days of great holidays first passed through Propylaea. This building with columns served as the front gate. In the side outbuildings were the spiritual treasures of Athens: an old library and an art gallery. A small but very beautiful temple was built right there. Goddess of Victory - Nike .     Parthenon Temple of Athena Pericles, the famous ruler of Athens, under whom this Greek Kremlin was built, said very well about the Parthenon: “We love wisdom without effeminacy and beauty without whimsicality.” And, indeed, the sacred house of the Virgin Warrior is distinguished not by decorations, but by its severity and grandeur.  The last masterpiece of the Acropolis was the temple of Poseidon and Athena Erechtheion . According to legend, the temple stood on the site of the dispute between Athena and Poseidon. An ancient olive tree grew near the temple. The Greeks believed that it grew from the shaft of Athena's spear.    The main type of temple in Greek architecture was peripter (feathered), that is, surrounded by columns around the perimeter  Order- the system of relationships between the bearing and bearing parts of the building (rack-and-beam system) entablature architrave capital column shaft stereobat  Order systems Doric Ionic Corinthian Tuscan Composite  The capital is the top of a column. The ancient Greek architectural theorist Vitruvius compared the Doric order "with the strength and beauty of the male body", as an expression of his strength, spiritual and physical. Sometimes, instead of a column in the Doric order, a male statue was installed, the so-called. atlas Doric order  The plasticity and proportions of the orders reflected the search for images in the likeness of the human structure. Volutes The Ionic order was compared by Vitruvius to "the sophistication of women, their adornments and proportionality." It is no coincidence that in the Ionic order columns were sometimes replaced by female figures, the so-called. caryatids.   Corinthian order The Corinthian order is the lightest, most slender of the three orders of the Greek system. In the time of Vitruvius, it was customary to symbolize the Corinthian column as an image of a beautiful girl, and the order itself as an expression of her tenderness and purity. flutes       Creative task. Design and draw a fabulous architectural order.      Resources used:
The material contains theoretical and historical information about the main five Greek and Roman orders, colorful illustrations, illustrative examples and knowledge testing. The presentation was made in accordance with the topics of the lessons according to the program of B.M. Nemensky Fine arts for grades 5-9. Download:Preview:Cover sheet for the presentation The presentation "Order System" was compiled for students of the 8th grade in accordance with the topics of the lessons according to the program of the author B.M. Nemensky "Fine Arts Grades 5-9", Moscow "Drofa", 1998. And also this presentation can be used in extracurricular activities in fine arts, MHC, technology.
The capital of the composite order is supplemented by four Ionic currencies. Its proportions coincide in everything with the Corinthian order.   The famous symbol of ancient Greece Acropolis built by the genius Phidias on a high hill in Athens.   Acropolis in Greek means "Upper City". In ancient times, the Acropolis in Greece served the same purpose as the Kremlin in Rus': in a fenced area were the main shrines and treasures, the treasury of the state, Those who ruled the city were also located here. The acropolis consisted of several magnificent buildings. It was placed on a hill, as if specially created by nature - a steep hill with a flat top.  Citizens who rise here on the days of great holidays first passed through Propylaea. This building with columns served as the front gate. In the side outbuildings were the spiritual treasures of Athens: an old library and an art gallery. A small but very beautiful temple was built right there. Goddess of Victory - Nike .     Parthenon Temple of Athena Pericles, the famous ruler of Athens, under whom this Greek Kremlin was built, said very well about the Parthenon: “We love wisdom without effeminacy and beauty without whimsicality.” And, indeed, the sacred house of the Virgin Warrior is distinguished not by decorations, but by its severity and grandeur.  The last masterpiece of the Acropolis was the temple of Poseidon and Athena Erechtheion . According to legend, the temple stood on the site of the dispute between Athena and Poseidon. An ancient olive tree grew near the temple. The Greeks believed that it grew from the shaft of Athena's spear.    The main type of temple in Greek architecture was peripter (feathered), that is, surrounded by columns around the perimeter  Order- the system of relationships between the bearing and bearing parts of the building (rack-and-beam system) entablature architrave capital column shaft stereobat  Order systems Doric Ionic Corinthian Tuscan Composite  The capital is the top of a column. The ancient Greek architectural theorist Vitruvius compared the Doric order "with the strength and beauty of the male body", as an expression of his strength, spiritual and physical. Sometimes, instead of a column in the Doric order, a male statue was installed, the so-called. atlas Doric order  The plasticity and proportions of the orders reflected the search for images in the likeness of the human structure. Volutes The Ionic order was compared by Vitruvius to "the sophistication of women, their adornments and proportionality." It is no coincidence that in the Ionic order columns were sometimes replaced by female figures, the so-called. caryatids.   Corinthian order The Corinthian order is the lightest, most slender of the three orders of the Greek system. In the time of Vitruvius, it was customary to symbolize the Corinthian column as an image of a beautiful girl, and the order itself as an expression of her tenderness and purity. flutes       Creative task. Design and draw a fabulous architectural order.      Resources used:
slide 1 slide 2  About the Greek house of the 6th and 5th centuries. BC. little is known. We know that it had a very modest size and a simple design. Several rooms, where they cooked, dined, washed and slept, surrounded the courtyard, through which the rooms were illuminated. In the front rooms, the floors were often decorated with mosaics; utensils, especially ceramic vases, were distinguished by the refinement of forms and the subtlety of painting. All the achievements of ancient Greek architecture are associated with the construction of temples. The Olympic gods, wise and perfect, must also have worthy dwellings - temples. Residential buildings (even of the richest citizens) were fragile and modest. residential architecture About the Greek house of the 6th and 5th centuries. BC. little is known. We know that it had a very modest size and a simple design. Several rooms, where they cooked, dined, washed and slept, surrounded the courtyard, through which the rooms were illuminated. In the front rooms, the floors were often decorated with mosaics; utensils, especially ceramic vases, were distinguished by the refinement of forms and the subtlety of painting. All the achievements of ancient Greek architecture are associated with the construction of temples. The Olympic gods, wise and perfect, must also have worthy dwellings - temples. Residential buildings (even of the richest citizens) were fragile and modest. residential architecture
slide 3  The temple, dedicated to the patron god of the city, was built with the money of the city-polis and belonged to the whole society. Nominally remaining the dwelling of God, it served earthly, public purposes: it was the repository of the city treasury and artistic values. The temple was erected on the highest place, usually on the acropolis, dominating the city buildings, in the center of the city square, which served as a place for public meetings, festivities, and religious processions. The temple, dedicated to the patron god of the city, was built with the money of the city-polis and belonged to the whole society. Nominally remaining the dwelling of God, it served earthly, public purposes: it was the repository of the city treasury and artistic values. The temple was erected on the highest place, usually on the acropolis, dominating the city buildings, in the center of the city square, which served as a place for public meetings, festivities, and religious processions.
slide 4  HOMEWORK Write out the meaning of the terms in a notebook and indicate in the figure: Entablament - Base - Architrave - Frieze - Cornice - Metope - Flutes - Pediment - Triglyph - HOMEWORK Write out the meaning of the terms in a notebook and indicate in the figure: Entablament - Base - Architrave - Frieze - Cornice - Metope - Flutes - Pediment - Triglyph -
slide 5  TYPES OF GREEK TEMPLE Temple in Antes Prostyle Amphiprostyle - peripter - dipter - false peripter (double peripter) (Roman) TYPES OF GREEK TEMPLE Temple in Antes Prostyle Amphiprostyle - peripter - dipter - false peripter (double peripter) (Roman)
slide 6  Temple of Poseidon at Paestum The classic, most common type of Greek temple was the peripter (meaning "feathered") - a rectangular temple, surrounded on all sides by columns. An example of such a temple is the Temple of Poseidon at Paestum. Plan of a Greek temple. Peripter. Temple of Poseidon at Paestum The classic, most common type of Greek temple was the peripter (meaning "feathered") - a rectangular temple, surrounded on all sides by columns. An example of such a temple is the Temple of Poseidon at Paestum. Plan of a Greek temple. Peripter.
Slide 7  A - Doric, B - Ionic, C - Corinthian. The numbers show parts of the order: 1 - cornice, 2 - frieze, 3 - architrave (cornice, frieze and architrave together form an entablature), 4 - capital, 5 - column trunk, 6 - base. A - Doric, B - Ionic, C - Corinthian. The numbers show parts of the order: 1 - cornice, 2 - frieze, 3 - architrave (cornice, frieze and architrave together form an entablature), 4 - capital, 5 - column trunk, 6 - base.
Slide 8  Slide 9  As a result of the long evolution of the temple, an architectural system developed, later called an order (which means "order"). An order is a system of relationships between columns (bearing part) and entablature (bearing part). TOP PARTS OF THE ORDER: ARCHITRAVE FRISE CORNICE form an ENTABLEMENT As a result of the long evolution of the temple, an architectural system developed, later called an order (which means "order"). An order is a system of relationships between columns (bearing part) and entablature (bearing part). TOP PARTS OF THE ORDER: ARCHITRAVE FRISE CORNICE form an ENTABLEMENT
slide 10  a column placed on a base or without a base, standing on a stylobate (upper slab of a stone base); the column is decorated with a capital, on which the supporting beam - architrave rests, which, together with a decorative frieze and cornice, forms an entablature. The Greek architectural order consisted of the following elements: a column placed on a base or without a base, standing on a stylobate (upper slab of a stone base); the column is decorated with a capital, on which the supporting beam - architrave rests, which, together with a decorative frieze and cornice, forms an entablature. The Greek architectural order consisted of the following elements:
slide 11  DORICA ORDER In the era of archaism, the order developed in two versions: Doric and Ionic. Temple of Athena at Paestum. Built around 570. The Doric order developed in the Peloponnese and in the Greek colonies in Sicily and southern Italy. DORICA ORDER In the era of archaism, the order developed in two versions: Doric and Ionic. Temple of Athena at Paestum. Built around 570. The Doric order developed in the Peloponnese and in the Greek colonies in Sicily and southern Italy.
slide 12  DORICA ORDER The Doric peripter stood on a stone base - a stereobat (usually of three steps). The column, decorated with vertical grooves - flutes, did not have a base, it was completed by a simple round pillow, with a square slab above it. According to the Greeks, the Doric order is the embodiment of the idea of masculinity, rigor, simplicity. The columns of Doric temples were subsequently often replaced by male figures (atlantes). DORICA ORDER The Doric peripter stood on a stone base - a stereobat (usually of three steps). The column, decorated with vertical grooves - flutes, did not have a base, it was completed by a simple round pillow, with a square slab above it. According to the Greeks, the Doric order is the embodiment of the idea of masculinity, rigor, simplicity. The columns of Doric temples were subsequently often replaced by male figures (atlantes).
slide 13  IONIC ORDER Caryatids of the Erechtheion Temple The Ionic order is most widespread in Asia Minor and on the islands of the Aegean Sea. The shaft of an Ionic column was originally thinner than that of a Doric column, confirming its origin from a wooden structure. The Ionic column has a base. Temple of Nike Apteros IONIC ORDER Caryatids of the Erechtheion Temple The Ionic order is most widespread in Asia Minor and on the islands of the Aegean Sea. The shaft of an Ionic column was originally thinner than that of a Doric column, confirming its origin from a wooden structure. The Ionic column has a base. Temple of Nike Apteros
slide 14  IONIC ORDER The Ionic order was lighter, more elegant, and more elegant. The slender colonnade had a base at its base and was decorated with a capital in the form of two graceful curls, which are called volutes. Columns of the Ionic order were often replaced by female figures (caryatids). IONIC ORDER The Ionic order was lighter, more elegant, and more elegant. The slender colonnade had a base at its base and was decorated with a capital in the form of two graceful curls, which are called volutes. Columns of the Ionic order were often replaced by female figures (caryatids).
slide 15  CORINTHIAN ORDER in the era of the classics, the third order was developed - Corinthian, close in proportion to the Ionic, but even more slender and festive. CORINTHIAN ORDER in the era of the classics, the third order was developed - Corinthian, close in proportion to the Ionic, but even more slender and festive.
slide 16  CORINTHIAN ORDER By the end of the 5th c. BC. a third architectural order arose, the Corinthian. Its columns are as graceful as those of the Ionic order, and the entablature is more magnificent. The Corinthian capital resembles an inverted bell, composed of two rows of acanthus leaves with spiral vine tendrils at the corners. CORINTHIAN ORDER By the end of the 5th c. BC. a third architectural order arose, the Corinthian. Its columns are as graceful as those of the Ionic order, and the entablature is more magnificent. The Corinthian capital resembles an inverted bell, composed of two rows of acanthus leaves with spiral vine tendrils at the corners.
slide 17  slide 18  HOMEWORK: The Greek architectural order was used not only in ancient architecture, but also became the main element of Renaissance, Baroque, Classicism architecture. WRITE IN THE TABLE IN THE NOTEBOOK THE HISTORICAL BUILDINGS KNOWN TO YOU, WHERE THE SYSTEM OF GREEK ORDERS IS APPLIED ON THE LEFT, AND THE YEAR OF CREATION ON THE RIGHT. HOMEWORK: The Greek architectural order was used not only in ancient architecture, but also became the main element of Renaissance, Baroque, Classicism architecture. WRITE IN THE TABLE IN THE NOTEBOOK THE HISTORICAL BUILDINGS KNOWN TO YOU, WHERE THE SYSTEM OF GREEK ORDERS IS APPLIED ON THE LEFT, AND THE YEAR OF CREATION ON THE RIGHT.
slide 19  Son of Kronos and Rhea. Lord of the gods, progenitor of gods and people. Temple of Zeus at Olympia DEFINE TEMPLE TYPE AND ORDER Temple of Zeus at Olympia, built between 468 and 456 BC BC. architect Libon, had the value of a pan-Hellenic sanctuary and was the largest temple in all of Poloponnese. The temple is almost completely destroyed, but on the basis of excavations and descriptions of ancient authors, its general appearance can be reconstructed quite accurately. Son of Kronos and Rhea. Lord of the gods, progenitor of gods and people. Temple of Zeus at Olympia DEFINE TEMPLE TYPE AND ORDER Temple of Zeus at Olympia, built between 468 and 456 BC BC. architect Libon, had the value of a pan-Hellenic sanctuary and was the largest temple in all of Poloponnese. The temple is almost completely destroyed, but on the basis of excavations and descriptions of ancient authors, its general appearance can be reconstructed quite accurately.
|
| Read: |
|---|
New
- Wage formation factors
- Ultrasonic parts cleaning and degreasing - RUSDORF
- Breeding worms and obtaining biohumus
- Thesis: Profitability of the banking business: assessment and management
- Using reporting for risk analysis and assessment
- Inside view: a day in the life of a criminal investigation officer
- What happy and successful people always ignore
- Do you need to be happy all the time?
- All unhappy people are unhappy for one reason Feelings of happiness and joy in words
- Voronezh ufologist has published a book with personal photos of anomalous phenomena