|
Quail is a tender and delicious meat. And quail eggs are a dietary product that can be consumed by everyone from young to old, even allergy sufferers and people after serious illnesses. Keeping quails is no more difficult than any other poultry. And in small quantities it can be kept even in an apartment. We are preparing the room. Keeping quails requires a warm, dry room, with good ventilation, but without drafts. The optimum temperature for keeping quails is 20-22 degrees. Fluctuations of 16-25 degrees are acceptable. Quails do not like bright light, so the cells are not placed opposite the window. But at the same time, daylight hours should be 16-17 hours (with the help of additional lighting), if the lighting is less than 12 hours, this affects egg laying. Cages are placed in such a room: it can be in one row, or you can make racks and place them on several “floors”. We choose a cell. The type and size of the quail cage depends on the number of birds and the way the cages are placed. You can make them yourself or buy ready-made ones from quail breeders. Incubator. When breeding quails, this is a necessary thing, since they, unlike chickens, do not incubate eggs themselves. You can also buy it, or you can make it yourself. It is immediately necessary to take care of the electricity, especially if you often experience power surges or blackouts.

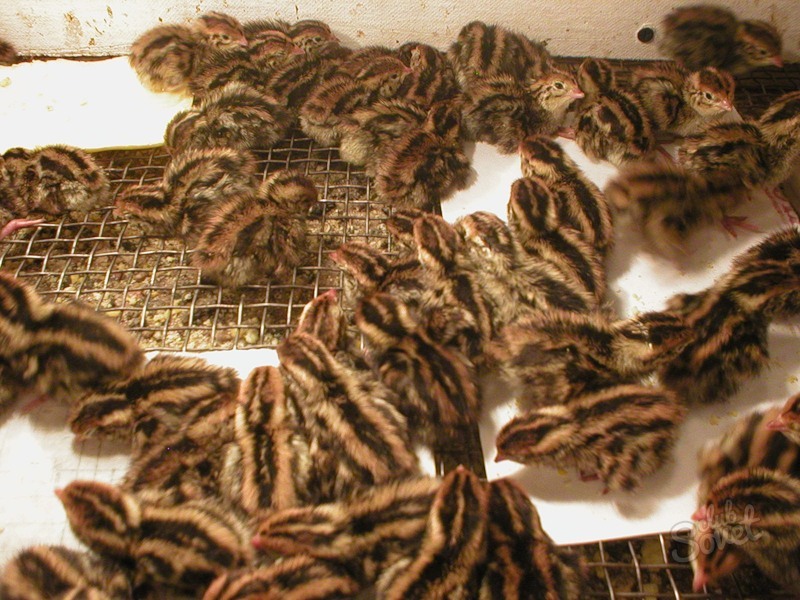
It is best to start breeding quails with the purchase of adult birds. But if you decide to start by buying eggs, then you need to consider that the eggs from the store will not work, they are not fertilized. During transportation, the internal structure of the eggs is disturbed, and this leads to a decrease in the percentage of brood: the greater the distance, the lower the percentage. If you decide to buy ready-made chicks, then you should have a room for keeping, cages, food, drinkers, etc. ready. The incubation period is 17 days, the hatching of quails is active and ends in 4-6 hours, although individual quails from the same batch can hatch 1-2 days after the main hatching. This is a departure from the norm. Hatched quails weigh 6-8 g, are covered with brown fluff with light longitudinal stripes on the back, they are very active. 
Healthy quails are kept in plywood or cardboard boxes - brooders, their size depends on the number of chicks. They must be clean, the bottom is covered with paper, which changes as it becomes dirty, and a 5 by 10 mm grid. The net prevents the phenomenon of "twine" in chicks - it serves as a stop and prevents the paws from moving apart. Lighting should be around the clock for continuous feeding. Several incandescent lamps are placed above the boxes, they serve both for lighting and for warming the young.

It is very important to maintain a stable temperature within 20-22 degrees, otherwise the chicks will die. From the first hours of life, quails are able to feed on their own. Since they grow and develop very quickly, they require feeds with a high content of protein, vitamins and minerals. Therefore, it is best to feed with special compound feed from the first days. In two months, the chick increases its mass by 20 times and almost reaches the size of an adult bird.

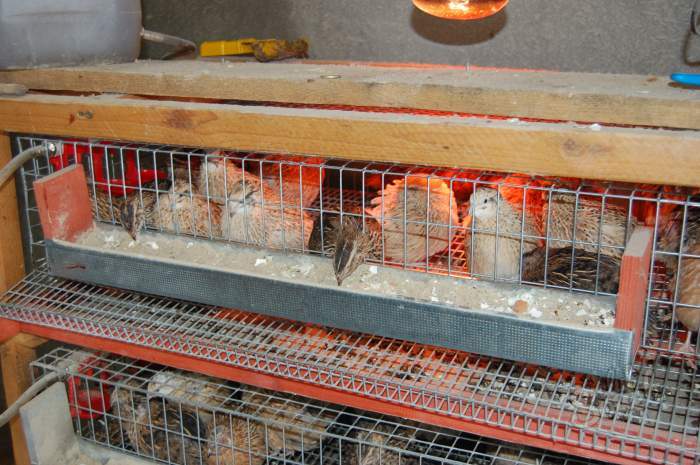
When keeping quails in order to obtain food eggs, cages up to 20 cm high are usually used. The bottom area depends on the number of quails placed in the cage and is selected at the rate of 180-200 square meters. see one head. If you need diet food eggs (i.e., unfertilized), then only hens can be kept in the cage. They will rush in the same way as with a cockerel.

For feeding, feeders are used in the form of a trough, attached from the outside, or automated (for dry feed). The main component of the feed is crushed corn and 15 percent of all types of cereals with small or crushed grains, egg feed, greens. Feed is sprinkled systematically, as it is eaten.

Water must be present constantly, if the drinkers are automated, then the water in them is changed at least 1 time in 4-5 days, the drinkers are thoroughly washed. Periodically, it is necessary to put a bowl of sand in the cages, where the quail bathe.

Thus, growing quails is not difficult, especially in small quantities. The main thing is to decide for what purpose you breed them: eggs, meat, chicks. And, having decided, prepare all the necessary devices, and you can safely get down to business.
The Japanese from ancient times (14th century) learned to breed quail at home. Breeders, however, paid attention to this bird only at the beginning of the 19th century and bred a breed that is now known as the “Japanese quail”.
Outwardly, the “selection” quail practically does not differ from the wild one in any way. There is a big difference in productivity. If a wild female enters puberty only at the 12th month, then the domestic one begins to rush at 35-40 days and can produce about 300 eggs per year. Japanese quail weight: males - 120, females - 140 g.
Domestic quail originated on farms in many countries. They managed to bring the live weight of quails up to 230 g, and some females - up to 300 g or more. This is how much the quail of the Pharaoh breed, which was bred in the USA, weighs. The egg production of meat quails is, of course, lower than that of egg quails, but not significantly.
Breeding this bird is quite a profitable business. Five females by weight produce the same number of eggs as one hen. But what a difference in precocity! The quail grows three times faster than the chicken, and consumes less feed. The quail is distinguished by a rapid change of generations and very high productivity.
Quail eggs are much tastier and much healthier than chicken eggs. They have more vitamins A, B1 and B2, iron, potassium, cobalt, copper and essential amino acids. They can be eaten raw, boiled, fried and pickled. In Japan, quail eggs are a staple in schoolchildren's diets.
It is worth noting that quail droppings are a wonderful fertilizer. It is best to keep it dry.
Recently, many countries have begun to show interest in such a profitable business, especially since quails can survive the winter in an ordinary apartment. Small cages with cute and moving birds fit well into the interior of the apartment. They take up little space. In the summer, there is absolutely no trouble with them, they need a little space. In order to have quail meat and eggs in abundance on the table for one small family throughout the warm period of the year, two males and four females can be left for the winter.
How to breed quail
In general, select the freshest eggs for incubation. If you did not mark the date of their demolition, dip in water at room temperature. Fresh full-fledged eggs will sink to the bottom. It is better to store them no more than 8-10 days at a temperature of 2 to 15 ° and air humidity of 60-70%. Take eggs for incubation clean, not very dark and not too light in color. It is better to choose eggs from females aged 2-6 months. If there is no incubator and female hens, then eggs can be laid under chickens, for example, benthams. The incubation mode is as follows: temperature - 37.5 °, humidity - 65%, turning the eggs - after 1-6 hours for 14 days. Then the trays can be transferred to the output chamber.
The duration of incubation is 16.5-17.5 days. At the time of pecking and hatching, it is better to increase the humidity a little so that the shell membrane is not so dense. Under these conditions, hatching is friendly, usually in 4-6 hours. A little ozonation of the air is useful: it helps the development of embryos.
At first, quails need a high temperature: for daily - 37 °, week - 35 °, two-week - 31 °, three-week - 27 °, four-week - 21 - 25 °. Then you need to maintain a temperature of 19-21 ° at a humidity of 55-60%. For heating in the first two weeks, you can turn on the lamps around the clock, and then for 14-15 hours a day. It is better to turn on and off the light at the same time. The quail is occasionally watered with a slightly pink solution of potassium permanganate. They usually feed 4 times a day. The first week is given by quail or chicken eggs, hard-boiled and grated along with the shell. You can also add ground compound feed, boiled fish, crushed crackers, from three days - live food.
Chicks do not tolerate dampness, drafts, sudden changes in temperature. Their cage should always have clean sand and water.
Approximately 8-9 kg of feed is consumed per quail per year, and 0.8 kg for growing up to slaughter age. Compound feed for an adult bird is spent approximately 25 g per day.
To obtain food eggs, females can be kept without males, and for incubation, I leave about 2-4 females per male. Good mating results occur when two females are in one cage, and one male is in the other. In the morning I put one female to the male for 15-20 minutes, and two hours later - the second.
An adult bird can be fed 2-3 times a day. She should receive a flour mixture - 12 g, protein feed (cottage cheese, fresh fish, minced meat, etc.) - 10 g, succulent feed - 10 g. It is good to give vitamins A, D3, E. Quail feed is used both in dry and and wet. Greens can be given without restrictions. Twice a week, you can add boiled liver to the feed. Japanese quail prefer sweet and sour foods.
At three weeks of age, females can be distinguished from males. The males have a dark brown chest and brown neck, there is a tubercle in the upper part of the cloaca, and the skin around it is light pink. Females have a white neck and a gray chest with black spots. The skin of the cloaca is bluish-gray.
Monthly young animals are separated by sex: extra males - for meat, and females - for oviposition (they rush for 10-12 months, after which they begin to fatten them).
Equipment for keeping quails
It is better to have a small-sized incubator in your household (Fig. 1).
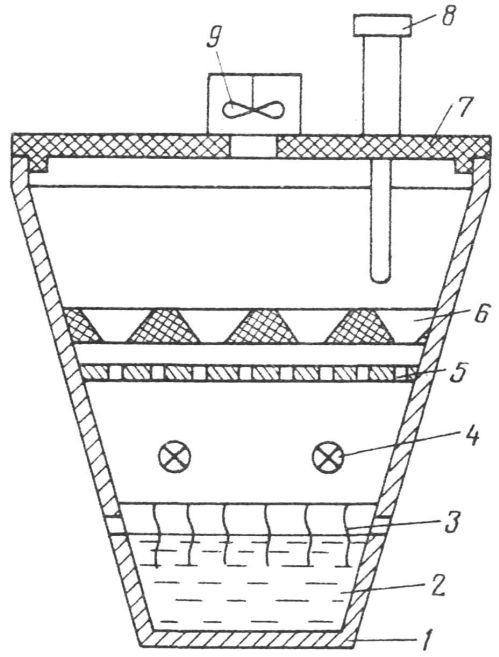
Rice. 1 Scheme of a small-sized incubator:
1 - reservoir (bucket); 2 - water; 3 - filtering; 4 - incandescent lamps; 5 - metal partition; 6 - egg tray; 7 - reservoir cover; 8 - electrocontact thermometer; 9 - fan
Holes with a diameter of 10 mm were drilled in the walls of a cone-shaped polyethylene bucket at a height of approximately 80 mm. They are necessary to limit the level of water being poured and to ventilate the workspace. By changing the level and area of the water mirror, as well as the depth of immersion of the filter paper, the humidity is regulated. The heat source is excellently served by two incandescent lamps with a power of 15 W each, and a metal partition with holes made as a safety grill and heat accumulator. The cover contains an electric contact thermometer and a fan. Include once within 1-2 days. For thermal control, a circuit with a thyristor key is used, which, unlike circuits with an electromechanical relay, operates silently. The RT-1 thermostat, complete with an electric contact thermometer, has proven itself well.
Energy costs can also be reduced if the bucket is wrapped with heat-insulating material. But the design without insulation is convenient because through the transparent wall of the bucket, you can easily control the state of all elements of the incubator.
Rice. 2 Automatic feeder made from cans
Small cells can be placed in several tiers. Their floor area is determined at the rate of 80-110 cm2 per bird. The height of the cells is 200 mm. With a multi-tiered cage, it is better to make it a little higher, so that it is more convenient to care for the livestock. For young animals, cages are made from a mesh with a cell of 10x10 mm. In the first week, the mesh floor is covered with a cloth, thick paper or a plastic mesh. Under the drinker at this time, you can use inverted glass jars placed with a gap on a saucer. Then it will be more convenient to have a pipe with a diameter of 30 mm with drilled holes, connected to a vacuum drinker. The depth of the water layer is 15 mm.
Feeders-grooves are hung outside with a length of 7-10 mm per bird. To make it more convenient for the quail to get food, the distance between the bars on the groove should be at least 20 mm. You can change the size of the feed gap with a rubber hose placed between the bars of the grate.
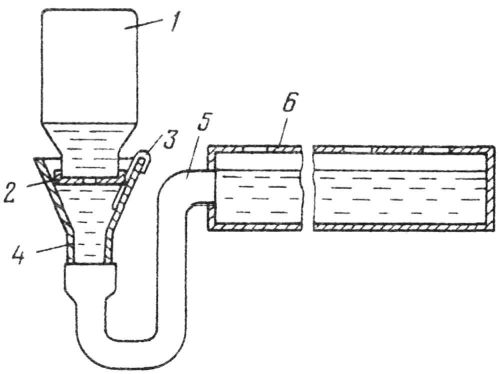
Rice. 3 Automatic drinker:
1 - glass three-liter jar; 2 - polyethylene cover; 3 - overlay; 4 - funnel; 5 - rubber hose; 6 - tube with holes for drinking
The mesh floor in the cages is made with an angle of inclination to the feeder of 5-7 °. At the edge of the floor is an egg collector lined with soft material. There should be a litter tray under the floor. Cells are illuminated thanks to incandescent lamps with a power of 25-40 watts. Bright light is not desirable because it can lead to pecking.
Recipe for a dish especially useful for people with a diseased liver
Wash the carcasses, salt, pour hot milk and cook over low heat until fully cooked. Tasty quail baked in Uzbek style. Carcasses are placed in warm salted water for one hour. Crushed spices, including also black pepper, coriander, are sifted through a sieve and sprinkled with this mixture of meat. After that, they are wrapped in parchment paper, placed on a baking sheet and baked for about 35-40 minutes, pouring water over the paper so that it does not burn. Delicious served with fresh vegetables.
|
P quail farm
Keeping quails at home is no more difficult than any other poultry. With a small number, they can be kept even in a city apartment, in cages for parrots or canaries. Maintenance and care of them is quite simple. The only condition for normal quail egg production is compliance with the conditions of detention (temperature and light conditions), as well as the use of specially balanced, high-protein feed. Otherwise, they are quite unpretentious birds.
If you want to start breeding quails yourself at home, then the first thing you need to know is that domesticated female quails have lost their incubation instinct, so artificial egg incubation is used to hatch young animals, so you will need an incubator.
For the incubation of quail eggs, any small-sized household incubators of the systems are used: "Universal", "Nat", IPH, ILU-F-03 and others. Such incubators can be purchased at any market or specialty store.
The capacity of these incubators is different, and is usually indicated based on the number of chicken eggs. Quail eggs in such incubators can enter 4 - 6 or more times more than chicken eggs. So, for example, 370 - 395 Japanese quail eggs are placed in the "Universal-45" incubator tray. For many amateur poultry farmers, the use of commercial home incubators for incubation of quail eggs may not be practical, since such incubators are too large for their needs. Therefore, for those who grow young quails in small quantities, home-made incubators of a smaller capacity will be more suitable.
The incubation period for quail eggs is 17 days (for chickens - 21). The hatching of quails is active and ends in 4 - 6 hours, although individual quails from the same batch may hatch 1 - 2 days after the main hatching.
Freshly bred common quail quails are covered with brown down with two light stripes along the back. They are very mobile, although their mass at this time is only 6-8 g.
Healthy quails are grown in plywood or cardboard boxes. The size of the boxes depends on the number of quails. If you have a small number of quails and the entire output is 20 - 30 quails, then any suitable plywood box can be used for these purposes, for example, a standard mailbox. But if you are going to seriously engage in quail breeding, and therefore - independently and constantly breed your chicks, then it is better for you to make a universal brooding box.
The boxes must be clean, the bottom must be covered with clean paper, which must be changed as it gets dirty. The quail from the incubator is immediately planted in a box, at the bottom of which there is a grid with a cell of 5 x 10 mm. This excludes the appearance and development of the so-called "twine" in quails, when the legs of the quail begin to move apart in different directions (the mesh at the bottom allows this to be done, being an emphasis for the legs).
Temperature control is very important. Quails are very sensitive to temperature drops and the slightest cooling leads to increased mortality of young animals.
From the first hours after hatching, quails are able to feed on their own. In general, the whole life of these birds, from the very first day, is aimed at absorbing and searching for food. Due to their very rapid growth and development, they require feeds with a high content of protein, vitamins and minerals. In the first days of life, they can be fed with finely chopped boiled eggs, cottage cheese, sprinkled with breadcrumbs, chopped herbs, as well as bird feed for young animals aged from 1 to 10 days.
Quails grow very quickly. In two months, they increase their mass by more than 20 times and practically reach the size of an adult bird. For comparison, during the same period, chickens increase their mass by only 14 times, but before an adult bird, they still grow and grow ...
When keeping Japanese quails in order to obtain food eggs, cages up to 20 cm high are usually used. The bottom area depends on the number of quails placed in the cage and is selected at the rate of 180 - 200 square meters. see one head. If you need dietary food eggs (i.e. unfertilized), then only hens can be kept in the cage. They will rush in the same way as with a cockerel.
For rational use of space, usually several of these cells are placed one on top of the other (such as a rack). Like all chickens, these quails willingly bathe in dry sand, which must be taken into account when keeping them and periodically put a bath with a layer of sand 5–7 cm thick in a cage for this purpose.
The room in which the cages for quails are installed should be warm, dry, with good ventilation, providing fresh air.
The intake of fresh air should not be accompanied by a draft. One of the first signals of the presence of drafts is the loss of feathers in birds.
In rooms where adult quails are kept, the relative humidity of the air should be in the range of 55 - 75%. 60 - 70% is considered optimal.
The temperature is maintained at 20 - 22°C, fluctuation from 16 - 25°C is acceptable.
Japanese quails are fed with all kinds of grain feeds with fine or crushed grains, egg feed and greens. They eat well compound feeds with a high protein content, which has a positive effect on their productivity. Feed is added to the feeders regularly, as they are eaten.
Quails are fed 2-3 times a day. Feeders and drinkers in the form of ordinary gutters that strengthen the outside of the cells. For dry feed mix, it is advisable to use automatic feeders. In the bunker, which is attached above the cells, the dry mixture is poured for a day, or even for several days. As it is eaten, the feed from the hopper is poured through the tubes into the feeders.
For watering, you can also use automatic drinkers, their preparation is quite simple - according to the principle of communicating vessels. Water can be poured into them for several days, but at least once a week, before refilling with water, the drinkers should be thoroughly rinsed.
For succulent feed, you should have an additional feeder, also reinforced from the outside.
When keeping 100 female quails, the daily feed consumption is 2.5 - 3 kg. About 90 kg of feed will be required for a month. During this period, quails will lay 2200 - 2300 eggs.
Quail Raising Guide
Quail common (genus Coturnix coturnix) - a bird of the pheasant family, chicken order. He is the smallest representative of the chicken order. The length of his body is 16 - 20 cm, weight - 80 - 150 g.
Plumage color - brownish - brown, with light spots and strokes. In males, the color of the goiter and around the eyes is red, in females it is lighter. This is clearly seen in this photo - on the left is a male cockerel, on the right is a female hen.
Common quail is common in Europe, Africa and Southwest Asia: In Russia, it lives on the territory from the Black Sea to Lake Baikal. It is an object of hunting. It lives in fields, meadows, plains and mountains. Birds are very shy and it is very difficult to notice them in nature. They nest in open areas with developed grass cover. As a rule, the nest - a small depression in the ground - is found and equipped by the female herself. She also incubates the eggs and protects the chicks for the first days after hatching. In one clutch there are from 8 to 24 mottled, yellow-brown eggs, weighing 10-12 g each. The chicks hatch in 17-18 days and as soon as they dry out, they immediately begin to peck at the food. They grow very fast. After two weeks, they acquire a feather cover and are already beginning to try to fly from place to place, and by one and a half to two months they become completely adult independent birds. Common quail is perhaps the only migratory bird among chickens. With the onset of cold weather, it flies south.
In addition to the common quail, it is also called the European quail, and the mute or Japanese quail (Coturnix Japonica) also lives on the territory of Russia. It was domesticated in Japan in the late 19th and early 20th centuries and is the main bird on quail farms.
At present, several breeds of Japanese quail have been obtained by breeding: marble, pharaoh, etc., which are bred for the purpose of producing eggs and meat, both at home and on an industrial scale.
The live weight of domestic quail males is about 110 g, females up to 150 g. Japanese domestic quails begin to lay eggs at the age of 50 - 60 days (for comparison, chickens begin to lay eggs no earlier than after 180 - 210 days). Each quail can lay up to 300 or more tasty and healthy eggs per year, each weighing 10-14 g.
The production of quail eggs is cheaper than chicken eggs, and quail breeding is the most profitable poultry farming. A female quail with a live weight of 125 g, egg production of 250 - 300 eggs has an egg mass of 20 - 24 times more than the bird itself (for chickens, 8 times). In addition, quails serve as "suppliers" of high-quality meat, which is considered a dietary product. No wonder in Russia quail dishes were considered royal food.
In order to breed domestic quail breeds in many countries since the middle of the 20th century. specialized quail-breeding farms (farms) have been created, the profitability of which is quite high. Even specialized breeds of Japanese quail of different directions have been bred - egg-laying and broiler (meat). Broiler quails quickly reach a mass of up to 200 - 250 g, while the mass of egg-laying birds rarely exceeds 150 - 180 g.
Quail eggs are superior in many nutrients to chicken eggs. Five quail eggs, equal in mass to one chicken, contain 5 times more potassium, 4.5 times more iron, 2.5 times more vitamins B1 and B2. Much more vitamin A, nicotinic acid, phosphorus, copper, cobalt, limiting and other amino acids in quail eggs. Quails have more protein in their eggs than other brood birds. For example, in chickens, 55.8% of protein will be held in an egg, in quails - 60%.
In most brood birds, the egg shell is more than 10% of the mass of the entire egg, in quails - only 7.2%. The shell of quail eggs is pigmented, very fragile, but has a strong and elastic shell film. The color of the shell of quail eggs varies from very dark, yellow-brown to pure white. The density of quail eggs is less than the density of chicken eggs, which is obviously due to the lower relative mass of the shell.
Quail eggs are a concentrated biological set of substances necessary for a person, these are real health ampoules. There is evidence in the literature that in ancient times, quail eggs and meat were used in oriental folk medicine. This was one of the reasons for the domestication and selection of quails in Japan. Even in the time of the pharaohs in Egypt, medicinal properties were attributed to quail meat. In Japan, raw quail eggs mixed with orange juice are still used to treat asthma.
Quail eggs are a valuable food product that can be recommended in the diet of children and adults with a number of diseases. They do not cause allergic phenomena even in those people for whom chicken eggs are contraindicated.
In Central Asia, it is believed that the quail brings wealth and prosperity to the house where it is kept in a cage. In addition, quails are valued for their beautiful songs. In the old days, in the Kursk province they even kept domestic singing quails and for their songs they were valued no lower than the Kursk nightingales.
Breeds and varieties of domestic quail
At home, amateur quail breeders contain various types of quail. In Russia and European countries, these are mainly the following breeds of quail: Japanese, marble, British black and white, "Pharaoh", as well as various crossbreeds from crossing these breeds.
Japanese quail- got their name because they were bred in Japan and are successfully bred there to the present. Breeding of quails of this breed has been going on for more than a hundred years. One of the factors contributing to the development of this breed was the atomic bombings of Japanese cities, and as a result, the search for alternative food products that contribute to the removal of radionuclides from the body. Studies have shown that quail eggs are a natural product that maximizes the removal of radionuclides from the human body.
Quail breeding was aimed at increasing their egg productivity. The plumage color of domestic Japanese quails is the same as that of wild ones. The live weight of males is 115 - 120 g, sometimes up to 130 g. Females weigh an average of 138 g, and in some cases up to 150 g. They start laying eggs at the age of 40 - 60 days and can lay up to 300 eggs or more per year. The average egg weight is 9 - 11 g. They are undemanding to the regime of keeping and are resistant to a number of diseases. Most amateurs who are engaged in quail breeding breed Japanese quails.
marble quail- a mutant form of Japanese quail. Birds have a light gray smoky plumage without a pattern. In terms of productive qualities, marble quails belong to the egg type of quails. In terms of live weight and egg production, they differ little from Japanese ones.
British black quail have black plumage with a brown tint. This variety was obtained in England as a result of a mutation from Japanese quails. In terms of live weight, British black quails outperform Japanese ones by 5-7%, but are inferior to them in growth rates and egg production.
Quail breed pharaoh belong to the meat breed and have the same plumage color as the Japanese quail. The live weight of females is on average 235 g, with fluctuations from 160 to 310 g, and males weigh 200 g, with fluctuations from 160 to 265 g. Females begin laying eggs at the age of 40-50 days and lay up to 220 eggs per year, weighing from 12 to 18 g. These birds are effectively used for the production of quail - broilers. At 45 days of age, they reach a live weight of 150-180 g.
In England, the USA and other countries there are varieties of quails: American broiler albino, white English, English golden, tuxedo or tuxedo quail. But as a rule, they are all mutant forms from Japanese quails.
Where to begin?
So, you have seriously decided to breed quails. How to form a livestock, what costs are ahead and what, ultimately, you can earn on this. Read the answers to these and some other questions on this page.
First, a few general tips.
Do not attempt to incubate eggs purchased from grocery stores. This egg is unfertilized, the so-called diet, and, of course, nothing will come out of it ...
If you choose the option with incubation, then everything should be ready for you in advance, and the incubator, especially self-made, must be tested for accuracy and temperature stability. If you experience frequent power outages, consider how to keep your incubator running smoothly. Obviously, you will need a generator or incubator with battery backup. Fortunately, the industry produces such incubators. All this is due to the fact that the hatching egg has a short shelf life of 5-7 days, and besides, it is not known how much it has already been stored, so the egg will have to be immediately laid for incubation.
During transportation, the internal structure of the eggs is damaged. If you have transported an egg over a distance of more than 200-300 km, then be prepared for the fact that the hatchability is unlikely to exceed 50%. And this is with strict observance of all other requirements.
If you decide to buy 3-day-old chicks, then you should also have everything ready to receive them: a room, cages, food, drinkers, etc. This is due to the fact that young chicks are very demanding on food, and even small interruptions in nutrition can significantly weaken them. As soon as you deliver them, you should immediately transplant them into cages and start giving water and food.
When increasing the livestock, correctly assess your capabilities - keeping a large livestock (more than several thousand heads), although more profitable, is less profitable, because. there is a need for additional labor, transportation costs increase, requirements for premises, arrangement of cages, drinkers increase, the question arises of manure disposal, storage of feed, etc. In the event of a mass loss, the losses are much greater than with a small number of livestock. Although, this happens extremely rarely - it's not worth discounting it completely ...
Beginners are sometimes frightened by questions related to incubation, but they are all quite solvable. And after a while they cease to cause any serious difficulties. The main thing is to strictly follow the technology - after all, everything has long been known and described in detail on the pages of this site - and you will succeed ... Requirements for the premises
The room can be anything, the main thing is that it meets some basic requirements:
The room should be well ventilated - fresh air is a must! And keep in mind that quails do not like drafts and bright light. For this reason, you should not place the cage near the window. Bright light and flying birds cause stress in quails, which in turn is one of the reasons why they may stop rushing or begin to peck at each other.
It is important that the temperature in the room is not lower than +16°C - the optimum is about 18-20°C.
Lighting should be moderate for 16-17 hours a day. Daylight hours less than 12 hours lead to the cessation of oviposition.
You also need to exclude the access of other animals: birds, cats, dogs and other animals. There is no need for quails to worry too much. This reduces egg production and can still cause pecking.
cage requirements
There are no strict requirements for the structure of the cell, except, perhaps, for two important conditions:
The floor area of the cage per adult should be 100-120 sq.cm. With a tighter or more spacious content, they rush worse.
It is important that the height of the cage is no more than 20-25 cm. Otherwise, the quail, taking off, will pick up more speed and may get hurt on the top of the cage.
During the breeding of quails, the design, cell sizes and materials used in the manufacture have changed somewhat. I currently use double cages with a drinker in the middle. The design of the cage is quite simple, and it is not difficult to make them yourself.
In cages where quails are kept for meat, the floor does not have a slope, there is no egg collector. This is due to the desire to reduce the cost of materials and time for manufacturing. If, in addition to males, you left females for fattening, the collection of eggs in such cages, despite the absence of an egg collector, will not take much time, because. they will start to really rush from two months.
With a population of more than several hundred quails, as well as in cages with laying hens, it is still better to make an egg collector. The advantages of this design are obvious: egg collection is simplified, and the egg itself is much less dirty with droppings, which improves its presentation.
In the manufacture of cages, I use wooden bars with a section of 20x40 mm and a galvanized metal mesh. I make pallets from fiberboard, plywood, but it is better to use sheet (not corrugated) fiberglass - pallets from it are very durable. Other materials may also be used.
For the floor, a grid with a cell of 10x10 mm is best suited. In places of access to the feeder 20x40 or 20x50 mm.
To save space, the cells should be arranged in 3-4 tiers. It is advisable to place the first tier at a height of at least 80-100 cm from the floor. Quails do not like drafts, and even at a lower height, they would have to crawl on all fours when serving. You should not do more than 3-4 tiers. To get to the top cage, you have to stand on something, which is also very inconvenient.
And this is a variant of a decorative cage. Such a decorative cage can be placed in an apartment in the kitchen or balcony, or in the country on the veranda or in the gazebo. Incubator
The literature describes many options for self-manufacturing of incubators and thermal control devices. You can buy a ready-made industrial incubator, or, for example, purchase only a thermostat, and make the incubator yourself. In general, almost any incubator will do, the main thing is that it allows you to set and maintain the temperature regime within 37-39 ° C. Since quail eggs are much smaller than chicken eggs, in incubators designed for chicken eggs, quail eggs can be laid in one tray in two rows, while they will fit about three times more than chicken eggs.
Another necessary condition for successful incubation is the periodic turnover of eggs. It is good if the incubator automatically turns the eggs, otherwise you will have to do it manually 6-8 times a day, but not less than 4 times. If this condition is not observed, the chick sticks to the inner walls of the egg and will not be able to hatch.
Whatever incubator you use, industrial or self-made, please note that you will have to deal with such a phenomenon as the temperature difference between the upper and lower tray. Physically, this is explained by convection, i.e. warmer air rises and colder air sinks. To reduce this effect, a fan is mounted inside the incubator. But even the presence of a fan does not guarantee uniform heating, therefore, before using the incubator, it is necessary to control the temperature at least at two points: on the lower and upper trays. For large incubators, there may be more control points.
The temperature should be measured with a medical thermometer (it is more convenient to use two at once). Outdoor and indoor thermometers should not be used for this purpose, because. they do not give the required measurement accuracy. The control is carried out a few hours after the incubator is turned on, when it enters the operating mode. You can do several measurements, for example, in half an hour or an hour. Thus, you will not only know the temperature difference between the upper and lower tray, but also check the stability of maintaining the temperature over a long time. And do not forget that the medical thermometer must be “shaken off” before each measurement.
The maximum temperature difference should not exceed 2-3 °C, otherwise for some trays the temperature will go beyond the allowable 37-39 °C.
If, however, a significant temperature difference is observed, the design of the incubator should be analyzed and measures taken to reduce this effect. The reasons may be the following: insufficient fan efficiency; poor thermal insulation of the walls of the incubator; internal structural elements interfere with air circulation or the distance between the trays and the walls of the incubator is too small; too powerful heater. As the latter, conventional incandescent lamps of suitable power are often used. Using more lamps of lower power will achieve more uniform heating. In addition, lamps of lower power (25-60 W) tend to last longer than lamps with a power of 100 W or more.
In the incubator, it is necessary to maintain a certain humidity. A psychrometer is used to control humidity.
If such a factory-made device is not found, then two ordinary household thermometers, the so-called "dry" and "wet", are installed. The name speaks for itself: the bottom of the "wet" thermometer is wrapped with a thin layer of wet gauze. To keep the moisture constant, the other end of the gauze is lowered into a small container of water. Due to the evaporation of water from the surface of the gauze, cooling occurs, the temperature on the "wet" thermometer drops. The difference in the readings of such thermometers is the greater, the lower the humidity and, conversely, at 100% humidity, the readings of both thermometers are the same. To avoid salt deposits on the "wet" thermometer, it is recommended to use distilled water. There is a so-called psychrometric table, according to which, knowing the readings of thermometers, one can determine the humidity.
This is the scientific way, so to speak. In practice, it is enough to install trays or some other utensils with water at the bottom of the incubator. For normal humidification, it is necessary that the area of evaporation of water is about 2/3 of the area of \u200b\u200bthe floor (bottom) of the incubator. At first I used a psychrometer, but soon I became convinced that the water containers provided the necessary moisture, and this device was no longer needed.
During the hatching period, water trays must be removed or covered so that the chicks do not drown by falling into them.
Some, for moisturizing, use a design in the form of a dropper. A drop of water periodically falls on the fan, which drives the air inside the incubator, and this is how humidification is achieved. I myself have not tried this method, but I think that in this case it is necessary to use filtered or, at least, boiled settled water, otherwise salt deposits will soon appear on the details of the incubator.
During the last two days before hatching, more intensive moistening of the eggs is used.
On my farm, I use two industrial incubators as workers and one self-made incubator as a brood. Inexpensive available materials were used for its construction - timber, fiberboard, etc., the thermostat is of industrial production.
Incubation.
Obtaining hatching eggs.
To obtain an incubation egg, they contain the so-called incubation herd (or livestock). It is necessary, of course, that the egg be fertilized. To do this, they keep males and females together, and there are 3-4 females per male. A smaller number of females per male leads to excessive consumption of feed and usable area in the cells, and a larger number leads to a decrease in the percentage of fertile eggs, and as a result, a decrease in the overall percentage of hatchability. See How to tell a male from a female?
An egg for incubation is taken from birds from 2 months of age for 8 months. In the future, the percentage of egg fertility decreases, although the egg production is still quite high, so the egg from females older than 10 months is used as food. (At the age of about 12 months, egg production decreases, and females are slaughtered for meat. The meat of 2 and 12-month-old quails practically does not differ in taste).
Selection of eggs for incubation.
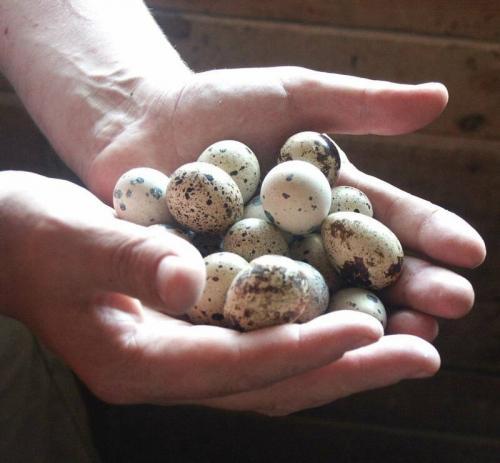
A medium-sized egg weighing 10-14 g is suitable for incubation. It must be intact, of the correct shape. A large egg is rejected because. it can be with two yolks. A small egg is also rejected - the quails from them are hatched less viable.
Storage of hatching eggs before laying in the incubator.
Despite the fact that the shelf life of food eggs reaches 3 months, the shelf life of hatching eggs is much less.
Before laying in the incubator, the egg is stored at a temperature not exceeding 22°C (optimally about 18-20°C) for 5-7 days, while the percentage of hatchability will be 85-90%. After 10 days - about 70%.
It is not advisable to store longer, as more and more embryos die in the egg, and the hatchability rate drops rapidly.
Bookmark in the incubator.
Eggs are placed vertically in the tray, blunt end up, in a checkerboard pattern. In trays designed for chicken eggs, quail eggs can be laid in two rows, and on the eve of hatching, transferred to hatching trays.
After filling the tray, it is advisable to disinfect the eggs. The most affordable method is treatment with a household ultraviolet emitter for 5-8 minutes. from a distance of 40 cm.
Temperature regimes of incubation.
The incubation period for quail eggs is normally 17 days. The following regimens are generally recommended in the literature:
|
Incubation days
|
Air temperature C.
|
Relative humidity, %
|
|
on a dry bulb
|
on a wet bulb
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15 - 17 (before pecking)
|
|
|
|
|
during withdrawal period
|
|
|
|
In practice, temperatures around 37.5°C can be maintained. This is due to the fact that the accuracy of household thermometers is low and it is impossible to measure the temperature with an accuracy of tenths of a degree. It would be nice to check the thermometer with a medical thermometer, the accuracy of which is much higher, before starting operation, and then take into account the error, which can be several degrees. I note that the medical thermometer itself is not suitable for continuous temperature control, since it must be "shaken" before each measurement. The presence of a control checked thermometer is necessary, even if the thermostat is manufactured industrially and has an installation scale, since the installation temperature may differ slightly from the real one. Good results can be obtained with a less stable temperature, but within 37-39°C.
Maintaining average temperature and humidity conditions is also due to the fact that in a large incubator, you have to put trays with eggs several times when the previously laid eggs are already incubated. In this case, the yield is slightly less than under optimal conditions, and is about 80%, which is quite acceptable. But the temperature should not be allowed to rise above 39 ° C, otherwise the embryos will die.
In the event of an emergency long power outage, you need to open the incubator and cool the eggs. This will save most of the embryos from death, but the hatching of the chicks will be delayed and last a little longer, sometimes 1-2 days.
With frequent power outages, which often happens in rural areas, it is advisable to take care of backup power in advance, i.e. about the generator.
On the 15th day, the eggs are transferred to the brood incubator or to the brood trays of the working incubator, where the eggs are already lying down and not so dense. From this point on, more intense moisturizing is applied, i.e. simply spray eggs from a spray bottle for flowers. Spraying is done twice a day, combining this procedure with periodic cooling of the eggs, which is continued for the remaining two days until hatching. This simple trick, suggested to me by one poultry farmer, softens the egg shell, it becomes easier for the chicks to hatch and, as a result, the percentage of hatchability increases.
For quail eggs, hatchability can reach 95% versus the usual 85-90%, but a more noticeable effect, when sprayed, is observed in relation to chicken eggs, additional moisture of which is also started two days before hatching. Here hatchability can rise from 60 to 90%!
If there were no significant deviations from the optimal regimes, on the 17th day the hatching of the chicks begins and ends after 4-6 hours. After that, the chicks are left in the incubator for another 4-6 hours so that they dry well, then they are transplanted into circles or into cages for young animals.
It is useful, in the process of incubation, to compensate for the uneven heating of the upper and lower trays, once a day, rearrange the trays in a circle, i.e. the bottom to the very top, the top - a little lower, etc. Thanks to this, the withdrawal starts almost simultaneously in all trays, and ends rather quickly, and does not stretch for 1-2 days.
Periodic cooling of eggs.
Eggs should be cooled twice a day, morning and evening, preferably at the same time. For what it is enough just to open the door of the incubator for 10-15 minutes.
Egg flip.
During the incubation period, it is necessary to turn the eggs 6-8 times a day. If the incubator does not have an automatic egg flip, then you will have to do it manually at least 4 times a day. Otherwise, the chick sticks to the inner walls of the egg and subsequently will not be able to hatch and will die.
If few chicks hatched...
There may be several reasons. Most likely, the modes of storage of hatching eggs or the temperature regimes of incubation were violated. Perhaps initially there was a low percentage of egg fertilization or the internal structure of the eggs could be damaged from shaking during transportation, if any.
Receiving eggs
To obtain eggs, an egg-laying population (herd) is formed. It consists mainly of hens older than 1.5 months of age. The presence of males is possible, but not required. Productivity does not suffer from this, in addition, it is believed that an unfertilized egg has a slightly higher nutritional value (so, in any case, it is stated in some sources). In addition, the absence of males is relevant when keeping quails in an apartment, since they “scream” quite loudly, and the females only “coo” softly.
Japanese domestic quails begin to lay eggs at the age of 30-40 days and lay about 250-300 eggs per year, i.e. egg production is 70-80%. This means that 100 layers will lay 70-80 pieces per day. eggs.
Please note that when changing the environment or food, the quail may stop rushing for 1-2 weeks.
After about a year, egg production begins to decline. If this indicator falls below 50%, then the layers are replaced with young ones, and the old ones are slaughtered for meat, because. further content becomes unprofitable.
Feeding laying hens is no different from quails, which are fattened for meat. Unless the feed is added first as the feeders are empty, small breaks in the feed do not affect productivity. In the latter, food is constantly present, which contributes to rapid growth.
About how much money will be needed to maintain 50 layers, and what benefits can be derived from this, read here.
Read about what dishes can be prepared from quail eggs here.
getting meat
To grow quails for meat, males should be separated from hens at the age of one month. (See how to tell a male from a female?) Cage density may be slightly higher than for laying hens (see cage requirements). Low lighting is used, food and water are constantly present.
Selection for slaughter begins from one and a half months, at first larger individuals are taken, and by two months all the birds remaining in this batch are slaughtered. Since quails reach their physiological maturity by two months, further maintenance is pointless (unless, of course, another goal was set besides obtaining meat), and leads to unjustified consumption of feed and production space.
12 hours before slaughter, feed and water should be removed so that the intestines of the birds are freed.
Slaughter is carried out by cutting off the head with scissors or secateurs. After all the blood has come down, you can start processing the carcass.
The carcass is scalded by dipping it for a few seconds in a container with hot water at a temperature of about 60-70 ° C. After that, the pen is easily plucked. If the water is too hot, then gusts of the skin are possible, from which the presentation of the carcass suffers.
It is much better to use paraffin for processing. To do this, take a sufficiently high vessel (bucket, pan, pot) and melt paraffin or wax in it. After that, the carcass is also dipped into it for a few seconds, then, after allowing the excess paraffin to drain, the carcass is left for a while until the paraffin hardens. After that, the paraffin along with the pen is easily separated. With this method, the processing quality is simply excellent.
If the water or paraffin is too hot, then gusts of the skin are possible, from which the presentation of the carcass suffers.
The carcass is gutted in the same way as any other bird.
For storage, the carcasses are placed in plastic bags, tightly tied or sealed so that the carcass does not freeze, and frozen.
I pack my products in plastic bags of 10 carcasses each, seal and freeze. The weight of such a package is about 1.1-1.2 kg.
Diseases
As sad as it is to realize, your domestic quails can get sick. In this case, I think you will need some advice from Dr. Aibolit (After all, he was a veterinarian!)
1. In order to prevent the disease in time, as well as to be able to effectively cure your pets, it is necessary to detect the disease as early as possible. And for this, do not forget to examine your pets every day, when feeding. Pay attention to the appearance of the bird, the condition of the feathers, skin, the mobility of the head, wings and legs.
2. The behavior of healthy birds is their daily state to which you are accustomed. Healthy quails are always active, move a lot, they have a good appetite. Their plumage is smooth, shiny, clean, has a bright coloring.
3. In sick birds, the feathers are ruffled, it can hardly stand on its feet, squat. There may be disturbances in the motor functions of the wings and legs. A sick bird sits alone in a cage, fluffed up, does not approach the feeders, its eyes can be closed.
4. If you notice that something is wrong with your quail, and its condition corresponds to any symptoms of the disease, then immediately isolate the sick bird from the healthy ones. To do this, place it in a separate cage, or a separate box - the infirmary. Give her first aid and be sure to consult a veterinarian. If possible, invite a veterinarian to your place, or take your bird to an appointment with him. And together with him, determine the measures for treating sick birds and preventive measures for healthy birds.
5. You should know that in birds, in particular in quails, all diseases are divided into non-contagious and contagious. Non-contagious quail diseases include various bird injuries, as well as diseases caused by violations of diets and diets, improper maintenance and care. These diseases are not transmitted through the air or through contact with sick birds. Infectious quail diseases are those diseases that are transmitted as a result of various infections. Mortality of birds with infectious diseases can reach 100%.
Quail suffer from contagious diseases much less frequently than other poultry. But it is impossible to completely exclude the possibility of their disease. As a rule, contagious diseases arise as a result of exposure to various infections caused by any pathogenic pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The causative agents of these diseases, under favorable conditions, can easily and quickly multiply in the body of a bird, and as a result, your healthy, full of life quail turns into a sick and sleepy bird. And the saddest thing about all this is that the mortality rate for contagious diseases can reach 100%. As a rule, infectious agents, fly larvae are concentrated in bird droppings, so timely cleaning of droppings is one of the preventive measures to prevent infectious diseases of your quails. Various antibiotics and antiseptics are used to treat infectious diseases.
Antibiotics are organic substances formed by microorganisms and have the ability to kill pathogenic microbes or prevent their growth. Antibiotics include: penicillin, tetracycline, streptomycin, oxyteraccycline, terramycin, biomycin, etc.
Antiseptics are antimicrobial agents. They are also used to fight pathogenic microbes. Antiseptics include: boric acid, furatsilin, hydrogen peroxide solution, rivanol, potassium permanganate solution and chloracid.
All non-communicable diseases can be divided into three groups:
- diseases caused by a violation of the diet;
- diseases caused by violation of the regime of detention;
- diseases caused by injuries, bruises and injuries.
DISEASES CAUSED BY DISORDERS
These diseases occur when the rules for feeding quails are violated. Incorrect composition of quail feed can deprive quails of essential vitamins and minerals. Or vice versa, an overdose of various mineral supplements and vitamins in the feed composition leads to excessive feeding with these substances. Both deficiency and excess of all this can cause various diseases in quails.
Violation of the formation of the egg shell
As a rule, the cause of this disease is an insufficient amount of minerals, calcium and vitamin D in the diet of quails. In this disease, quails lay eggs with a very thin and soft shell, or no shell at all, but only with an undershell film.
Treatment: Increase the mineral content of the quail diet. Add the required amount of chalk to the feed, as well as crushed shells. As a mineral substance, you can use crushed shells from quail eggs used for food.
Various beriberi
This disease occurs when there is a lack of vitamins of groups A, B, C, D in the body of quails. So, with a lack of ascorbic acid (vitamin C) in the body, there is a slowdown in the growth and development of young animals, a violation of feathering. In adult quails, egg production decreases, and the quality of the shell also deteriorates.
Treatment: add to the diet the required amount of food containing vitamins - fish and meat and bone meal, fodder yeast, green food.
Prolapse of the oviduct along with the egg
This disease can occur both as a result of malnutrition and as a result of improper maintenance. It occurs if, when keeping quails at the age of 30-45 days, full nutrition for an adult bird and intensive lighting are used, lasting 20-24 hours. In this case, early sexual development is stimulated and early egg-laying occurs (at the age of 30-35 days). In female quails who have not had time to frolic physiologically, there may be cases of loss of the oviducts along with the egg. In this case, as a rule, the quail dies. The same diseases can occur in adult birds with a lack of vitamins A and D2 in the diet.
Treatment: To eliminate this disease, add a double dose of vitamins A and D2 to the diet of quails during the week.
DISEASES CAUSED BY VIOLATION OF THE CONTAINMENT MODE
These diseases occur when the rules for keeping quails are violated. Violation of bird planting standards (as a rule, increased planting density of quails), bright light, placement of a cage with quails in direct sunlight or in a draft, non-compliance with the light regime or feeding regime can cause various diseases.
Manifestation of cases of cannibalism or pecking
The reason for the manifestation of this disease, as a rule, is the crowded content of the bird, as well as bright lighting. Quail behave restlessly, fight, peck at each other. Moreover, damage is usually done in the head area. If measures are not taken, then the damage caused by quails to each other can be such that they have a pecked head, eyes are pecked out, and some can be pecked to death. Often this is also manifested in the case of landing in a cage with females of a new male.
Treatment: First, isolate the injured bird in a separate cage. Reduce light and reduce planting density. Follow the full diet of quails, include fish and bone meal in it. For no reason, try not to regroup birds in cages (transplanting birds from one cage to another, i.e. from one group of quails to another).
Feather loss (bald patches)
This disease appears if there are drafts in the room for keeping quails, as well as at low air humidity (less than 50%). In quails on the back, feathers fall out on the head, islands of bald patches appear, that is, non-feathered areas of the skin. Feathers become brittle, the tips of the feathers are destroyed.
Treatment: Eliminate the causes of the disease (draughts and low humidity). For prevention, add B vitamins to the diet - fodder yeast. DISEASES CAUSED BY INJURIES, INJURIES AND INJURIES
These diseases usually appear as a result of the bird's fright and a sharp attempt to take off in a cage. In this case, the bird can be involuntarily injured on the roof or walls of the cage.
Injuries, injuries and fractures of bones.
These injuries occur when hitting a part of the cage. Depending on the severity of the injury, the decision to treat (or not treat) may be made. If, as a result of an injury, a bird has received an open fracture of a wing or paw, and it is not a breeding specimen, then it is better to put such a bird on meat. If the bird is of interest from a breeding point of view, then treatment can be tried.
Treatment: First of all, isolate the bird from the rest of the inhabitants of the poultry farm. In case of injury, carefully trim the feather around the wound with scissors. Treat the wound with a solution of potassium permanganate or furacilin. Lubricate the wound with tincture of iodine, and if possible, bandage the wound. After 2-3 days, unwind the bandages and inspect the wound, if necessary, lubricate with iodine again. In case of a fracture, carefully straighten the ends of the bones, disinfect the skin around the damaged area. Put cotton wool and a splint of thin sticks on the broken bone. Bandage everything carefully.
Questions and answers on this topic
Where can I buy quail or quail eggs for incubation?
Quails (or quail eggs) can usually be bought at the market, at a pet store (they are very rare) or at the zoo. You can buy eggs and try to hatch yourself. The only thing is that when buying eggs (in a store or on the market), find out if they are dietary (dietary - unfertilized, unsuitable for incubation).
Where can I buy cages for keeping quails and what is the price for them?
The cages for their maintenance are usually homemade, so the price for them is equal to the cost of the materials from which they are made + labor. You can use ready-made cages for poultry (parrots, canaries, etc.). In one cage with a bottom area of 20 x 40 cm, you can keep one family (3-4 hens and a cockerel).
In the area where I live 6-8 months of the year it is quite cold and only in the summer months it is warm (sometimes up to 35 degrees Celsius). Is it possible to breed quails in our area? Of course, quails will not be bred on the street, but in the garage.
In principle, quails can be bred in any climate zone. The only condition for their maintenance is the ability to provide positive temperatures in the cells. If you place quails in the garage, then you will need to insulate the area where they are located. After all, quails don’t really need natural light, they live quietly under artificial lighting.
If you breed quails in the garage, how are things going with the smell (from litter), with noise (from singing), and are there such or other problems?
If you clean the litter every two to three days, then there will be no smell from the litter. As for the noise from quails - it is not very big, only cockerels scream, if you keep only hens, then there is no noise at all. There are no other major problems either.
To start quail breeding, do I need to register as an entrepreneur?
If you keep a hundred or two of them, then I think it is not necessary to register. This is the same poultry as chickens, ducks, etc. If you breed in large industrial volumes (keep several thousand), then it will probably be necessary. But for this you will also need appropriate production areas, i.e. no longer a mini-farm, but an industrial farm.
Why angle the bottom of the cage?
The slope is needed so that the eggs roll towards the front wall. This eliminates the possibility that quails can crush them by stepping on them, and they also get less dirty with droppings, because they lie under the wall. Yes, and it is more convenient to get them when they are nearby, especially from the upper tier of the cage.
What water to give quails?
For quails under the age of 3 weeks, it is advisable to give boiled water. Older quails can be given tap water, raw, but settled. In addition, periodically (from once a week to 1 time per month - you choose for yourself) you need to add a little potassium permanganate to the water. Just a little, so that it has a slightly noticeable pink color. It is also useful to use any antibiotics for birds for prevention, for example, Brovaf.
Why do we need a partition that divides the cage into sectors, when it is possible to keep 30-40 quails in one cage, and make 2 doors (for the convenience of assembling eggs)?
You can keep everyone in one cage (without a partition), but when there are several sections, it is possible to place quails by age (usually with a small withdrawal of up to 20 pieces, just for one section); if necessary, it is possible to put one or the other from one section to another (after all, they also have incompatibility, when one another starts to hammer on the head, and seated the fighters in different sections - and the problem is removed.
How many percent can the correct light regimen influence when receiving eggs?
I didn’t count as a percentage, but if you make the lighting day - night (without a nightly 2-hour switch), then egg production decreases somewhat, this is for sure, it has been tested in practice. In addition, in the autumn-winter period, with a short daylight hours (without additional lighting), quails practically cease to rush.
How can you tell a hen from a cockerel in white or black quails?
Black quails have the same color as chickens and cockerels, so it is almost impossible to distinguish them by the color of their plumage. In traditional Japanese quails (brown), the male has a breast and neck, cheeks are reddish, as if scorched. It is possible to distinguish females from males in quails with a dark (as well as light - white) color by the following features:
- by observing them - firstly, the males scream quite loudly (pulling their heads up). In addition, the litter of cockerels will be colored with a white mass, so if it is deposited, then it is also possible to distinguish a chicken from a cockerel by the litter (although this is more difficult than to distinguish by crying, i.e. singing).
- having some experience, you can distinguish them by the structure of the cloaca. In a chicken, the opening of the cloaca is even, straight, and in a cockerel behind the cloaca there is a slight thickening, as a result of which the opening of the cloaca seems to be turned forward; To get a hatching egg, do I need to place a couple in a separate cage, or can I use those that will be obtained in the usual section?
To obtain an incubation egg, quails need to be kept by families: for 3-4 hens - one cockerel. In some literature I met a recommendation to keep the hens separately, and to plant the cockerel a couple of times a day for an hour, but I myself have not tried it. In principle, if you keep 1 hen and 1 cockerel in pairs, then the likelihood of getting fertilized eggs increases. However,
the cost of maintaining extra males increases, since in order to obtain the required number of hatching eggs, about 10 such pairs must be kept. And for this, it is necessary to equip the cages, for the appropriate number of pairs, and you need almost twice as much food. From personal experience - this winter I had two sections in the cellular battery free. And so I planted in one, (and then in another) a pair of quails (a hen and a cockerel). So, with such a landing, the hens rushed almost every day, giving out 25-27 eggs per month.
Although you can use for incubation and eggs that you will collect from the usual section. True, their fertility is lower, but there are more of them and you can win by numbers. The only condition for this: you need to observe the ratio of chickens and cockerels (3-4 chickens + 1 cockerel). Those.
if you have 12 hens in one section, then there must be at least 3 males.
Yesterday I hatched the first quails (what should I do) how should I feed them and with what?
Quail in the first days can be fed with hard-boiled quail eggs, finely ground corn, and cottage cheese. I prefer to feed quails up to 2 weeks of age with factory feed for young birds (up to 10 days). Feed must be added as it is eaten. When feeding raw food (cottage cheese, hard-boiled quail eggs), it is necessary to remove excess food that has not been eaten, because. it quickly sours and can cause an infection.
I have 106 females per day, 35 eggs on average (so the last week, but in general there were 60 eggs on average). Tell me what's the matter.
About egg production. If we take for the normal egg production of one quail - 22 eggs per month (30 days), then there should be 0.73 eggs per day. Therefore, 106 quails should produce about 70 - 73 eggs per day. But this figure is ideal, with strict adherence to diets and feeding norms, and
also content. If they give you 60 eggs on average, this is normal, and 35 is clearly not enough. There may be several reasons - first of all, food, daylight hours and temperature conditions. Try changing your diet and increasing daylight hours.
My quail began to rush at 3.5 months. This is fine?
On average, quails begin to lay in 2 - 2.5 months, but there are groups of quails that begin to lay later. It depends on the food and conditions of detention. At one time, I had quails, which were kept in enclosures, also did not rush until 3.5 months. Until he was seated in cages, they did not enter. Early egg production can be caused by the use of adult quail feed. In this case, they can begin to rush before 2 months. But this is fraught with the fact that the birds have not yet fully matured sexually, and some of them have a prolapse of the oviduct, as a result of which the bird dies.
How to make an incubation tray?
The tray is made of wooden (plywood) plates, 60-70 mm high and 8-10 mm thick. The size is selected depending on the depth and width of the incubator, as well as the number of trays in a row (one or two). The bottom is a welded galvanized mesh (24 x 24 mm), covered with a nylon mesh with a cell of 2 - 3 mm. As partitions between the laid quail eggs, you can use corrugated cardboard or fiberboard.
What is the ratio of males and females in the output, and are there "defective" females that do not carry eggs?
Regarding the ratio of males and females - according to statistics, on average they are 50 to 50, although in different conclusions this figure can fluctuate by 10 - 30 percent in one direction or another. Healthy females that do not lay eggs are usually not found, although there are females that rarely lay eggs (once every few days).
What ratio of chickens and cockerels is necessary for optimal quail egg production?
If you do not need hatching eggs, then you can not keep cockerels at all. To obtain a hatching egg, the ratio should be one cockerel to three to four hens. To obtain optimal egg production, it is rather necessary to maintain not the ratio of hens and cockerels, but the modes of keeping and feeding. Although if you keep a pair of quails (a hen and a cockerel) separately in a cage, egg production is the best, but such maintenance does not
justifies due to the increased consumption of feed.
Which quail eggs are more useful for nutrition - fertilized or not?
For nutrition - I think it doesn't matter, and for some recipes and treatment regimens, it is desirable to use only fertilized eggs.
How long can a quail lay after isolation from a cockerel?
Until he dies.
What conditions are necessary for quails during transportation (the nearest place for the possible purchase of quails is ~ 1000 km from the city)
Positive temperature in the cages, absence of drafts, strong shaking (vibrations), presence of light, water and food.
Is it possible to eat quail eggs together with the shell, does it increase calcium in the body and cleanse the body?
The use of quail eggs with shells really helps to increase the calcium content in the body. I can’t say anything about cleansing the body, I haven’t heard it.
How does the egg production of a quail depend on the number of birds in a cage?
To obtain optimal egg production, the floor area per quail should be from 180 to 230 cm2. With a decrease in floor area per quail, egg production decreases. A significant increase in area per head (for example, enclosures) also reduces egg production.
At what minimum ambient temperature do quails still lay eggs?
The optimum temperature for keeping quails is a temperature of 20 - 22 ° C, permissible fluctuations from 16 to 25 degrees. When you go beyond these limits, egg production drops. Regarding the minimum temperature: at one time, when I kept quails in an unheated room (barn), the temperature in the cage zone in winter was in the range of 5 - 12 ° C, while the quails continued to lay. There were cases when the temperature dropped to almost 0 ° C for a short time, but even at this temperature, individual birds managed to lay an egg, although there is no need to talk about mass production of eggs at such temperatures ...
Is it possible to use sea sand for bedding young animals.
I think not. Given that the young quail from the first day begins to actively eat and peck everything around, he will simply eat up this sand and die. For example, I generally refused bedding in my brooding boxes, I immediately plant the young on the mesh floor.
Is it possible to use mesh instead of plywood for the back wall and partition?
Can. It's just that if the cage is located near the wall and it has a plywood back wall, then the wall of the room is less polluted. In addition, the plywood back stack and baffle eliminate (or significantly reduce) drafts in the cage, even if there is active air circulation in the room. And quails do not like drafts very much.
Is it possible to make all parts of the cage and equipment from plastic.
I haven’t tried it, but it’s probably possible, the main thing is that these plastic parts provide: - structural rigidity, - hygiene (the bottom of the plastic mesh will probably get dirty faster), - normal access of the bird to the feeders (the cell size of the cage must be of the appropriate size). In addition, with a large cell size, the deflection of the rods should not be large in order to prevent the bird from crawling through them.
If it's not difficult, please also send the specification of consumables required for the manufacture of one copy of a three-tiered six-cell battery for 100 quails.
About the material:
- galvanized mesh for cages (24 x 40 mm) - 3.75 - 4 m (mesh width 1m);
- galvanized (or wicker) mesh for the bottom (10 x 20 or 10 x 10 mm) - 1.6 (1.8) m (mesh width - 1 m);
- plywood (or fiberboard) - 3 pcs. size 17 x 100 cm, 3 pcs. size 25 x 50 cm;
- corner 25 x 25 mm - 1 m;
- galvanized iron for pallets - 1.8 m (width - 1.1 m);
- round bar with a diameter of 12 mm (reinforcement) - 11.2 m;
- round bar with a diameter of 8 mm (reinforcement) - 29.5 m; *
·
This is the amount of materials used for the bottom of the wicker mesh cages. It requires a frame of 8 mm rod. If a welded mesh (10 x 20 mm) is used for the bottom, the amount of 8 mm rod can be reduced (up to 16 m).
In addition, the frame of the cell battery can be made of wooden slats. In this case, you can do without reinforcement.
Culinary recipes for quail
Since time immemorial in Russia, dishes have been prepared from quail meat. Old Russian cookbooks contain recipes for such dishes as quail with cherries, quail fried on a grill, quail with breadcrumbs. Lovers especially appreciate the delicate aroma and peculiar taste of quail meat, combined with juiciness and tenderness. Substances that give a specific taste to quail meat stimulate the appetite and increase the secretion of juice.
Recipes for cooking quail meat
Preparation of quail carcasses for the manufacture of culinary products and canned food
Before cooking dishes from quail meat, the gutted carcasses are washed with cold water and molded (of course, if the recipe does not specify otherwise). To do this, the wings of the bird are tucked into the back. To refuel the legs, the peritoneum is cut another 5-6 mm from the already existing longitudinal incision. First one leg is inserted into this incision, and the other under it. Then the carcass is rubbed with salt. After that, heat treatment of carcasses is carried out. They are fried over smoldering coals or in infrared ovens, deep-fried or baked in the oven. The frying temperature can vary from 150 to 230°C. The frying time depends on the temperature and the cooking method.
On our own, we add that quail meat is very satisfying and, despite the low weight of the carcass (only 110-120 g), 2-3 carcasses are enough for one serving.
Quail baked
The best way to heat treat young quails is roasting. At the same time, the meat turns out to be more juicy, tender and tasty. It is better to stew old quails in pans with a tight-fitting lid. Quenching is carried out at a temperature of 150-180°C. The meat is covered with a crust, as in the dry method of processing.
Deep-fried quail
Wash the carcasses and salt. In a saucepan with boiling fat (butter or ghee and margarine), place the carcasses so that they are completely covered with fat, cover the pan with a lid and bring to a boil. Then put the pan in the oven on medium and then on low heat for 50-60 minutes. To determine the readiness of the meat should be taken by the leg, it should be easily separated from the carcass. Before use, fry pieces of black bread in a pan in fat, in which quails were stewed. Put the fried bread on a dish, put the finished carcass on each piece of bread, decorate with herbs and serve hot.
Fried quail
Salt the washed carcasses and fry in a deep frying pan. Cover with a lid and place in the oven. On low heat, the quail will be ready in 40-50 minutes. Periodically, they must be watered with the resulting juice. Decorate the dish with hard-boiled quail eggs.
Quail stuffed
Quail 12 pcs.,
lamb 400 g,
onion 240 g,
egg 1 pc.,
cilantro greens 40 g,
spices and salt to taste.
The quail is plucked, singeed and carefully gutted, washed thoroughly in cold water, and the paws are chopped off. Put for 1 hour in a solution prepared from water, salt and red pepper.
Fatty lamb is passed through a meat grinder, finely chopped onion, raw egg, cumin, black pepper and chopped cilantro are added. All this is well mixed. Quails are stuffed with the resulting mass, placed in manti-kaskan and steamed for 35-40 minutes.
When serving, put 2 quails and a tomato salad in each plate.
Quail tobacco
Cut the washed carcasses lengthwise on the stomach, beat off, fill the legs into pockets. Salt, rub lightly with garlic, brush with sour cream and fry in a pan until golden brown. Tobacco quail go green salad and hot sauce.
Quail in milk
Wash the carcasses and lightly salt. Pour in hot milk and cook over low heat until tender. This dish is recommended for people with a diseased liver.
Grilled quail with spices
For 4 servings:
1 clove of garlic; salt;
1 teaspoon of cumin and coriander;
0.5 small onions;
1 st. a spoonful of finely chopped green coriander;
a pinch of ground cayenne pepper;
2 tbsp. spoons of olive oil;
8 quails;
grape leaves; parsley; lemon slices.
Place all ingredients except quails and garnish in food processor. Mix them into a homogeneous mass, coat the quail with it. Cover and leave for 2 hours. Grill, turning regularly, for 10-15 minutes, until the quails are cooked through and crispy. Serve on grape leaves, parsley and lemon slices. An oven can be used instead of a grill.
Quail in sour cream with cheese dumplings
20 quails;
200 g of oil for frying;
3 tablespoons of flour;
500 g sour cream;
250 g of cheese;
100 g of semolina;
4 eggs.
Salt the peeled, gutted and well-washed quails, fry in a pan in oil, browning well on all sides. Put in a saucepan, add broth, and simmer over low heat until fully cooked.
In the pan where the quail was fried, add flour, salt, mix well with the fat remaining from frying, pour 2 cups of broth, boil the mixture until thick, mix with sour cream, salt to taste and pour stewed quails with this sauce. Keep until steaming, without letting boil.
Serve with cheese dumplings.
Preparation of quenelles: grind the yolks, mix with grated cheese and semolina, salt, let stand for 2-3 hours. Then mix with whipped proteins and put on a wet napkin, giving the mass the shape of a roller. Wrap tightly in a napkin, tightly bandage the ends of it and, securing the edge with a thread, put the roll in boiling salted water. When the roll pops up, carefully remove it by unfolding the napkin. Cut the roll into round pieces, arrange around the dish with quails and pour over the sauce.
In addition to these recipes, quail meat can be prepared in the same way as the meat of other types of poultry.
Quail egg recipes
Quail eggs are eaten raw, boiled, fried or pickled. They are used in cooking for making omelettes, scrambled eggs and mayonnaise. Quail eggs are loved by children and willingly eat them. Children are attracted by the unusual color of the shell and the small mass. Quail eggs are very useful and do not cause side effects (diathesis) even in those people for whom chicken eggs are contraindicated.
Shelling boiled eggs
To peel hard-boiled quail eggs from the shell, you need to put them in a solution of table vinegar (2/3 vinegar and 1/3 water). After a few hours (about three hours later), the egg shell will completely dissolve. The remaining shell film is easily removed before use.
On our own, we add that after 20-30 minutes of such processing, the eggs completely lose their color and acquire a uniform white color. Such eggs can, for example, be dyed like Easter eggs.
pickled eggs
Put the peeled eggs in the marinade. The marinade must be clean, without herbs, otherwise the eggs will get an unpleasant dark or greenish tint. After 10-12 hours, the eggs are ready. They can be stored for several days. Before use, the film is removed and the eggs are strung on sticks to make it easier to take them.
Pickled eggs - 2
Quail eggs;
water 1 glass;
vinegar 1/2 cup;
black peppercorns 10 pcs.;
carnation 3 pcs.;
cinnamon;
sugar 1 tsp;
salt 1/2 tsp;
garlic 3-4 cloves.
The required number of eggs is boiled, cooled, peeled.
A marinade is made: water and vinegar, salt and sugar in equal proportions. It is brought to a boil, spices are added (to taste: peppercorns, cinnamon and cloves). After 2-3 minutes after the start of the boil, it is removed from the heat.
A few cloves of garlic, eggs are placed in a jar and poured with marinade. You don't have to roll up the banks.
After two days, the product is ready for use. Keep refrigerated.
Raw egg drink
Take 4-5 quail eggs, beat in a glass, add fruit juice, red wine or coffee, add honey or sugar to taste. This highly nutritious drink can be consumed daily.
Fried quail eggs
Break the eggs one by one into a hot, greased pan, fry over low heat, sprinkle with salt and finely chopped onion and pepper. Serve with fried potatoes or salad.
fried eggs
Boil hard-boiled eggs, peel, remove the film, beat 2-3 raw eggs into foam. Moisten hard-boiled eggs in beaten eggs, roll in breadcrumbs and fry in hot oil. Take out with a slotted spoon on a sieve, lay in a slide, garnish with parsley.
Omelette
Beat 12-15 quail eggs with milk (3/4 cup), add salt, finely chopped onion, and, if desired, sausage, ham, smoked fish cut into small cubes. Melt one tablespoon of butter in a frying pan, pour the prepared mixture, let it curl over low heat or in the oven. Serve hot.
Sandwiches with quail eggs
Spread thin slices of white or black bread with butter, cover them with a layer of finely chopped salted fish, and put quail eggs cut in half on top, sprinkle with finely chopped herbs and onions.
Quail eggs with rice or mashed potatoes
Put boiled, crumbly rice or mashed potatoes on a dish in the form of a circle, put eggs boiled without shells in the middle. Serve with sour cream sauce and tomato salad.
Quail eggs boiled without shell
To do this, add 1 tablespoon of vinegar and 1 teaspoon of salt to 1 liter of boiling water. Crack the eggs one at a time, drop them into boiling water and let them curdle for 2 minutes.
Quail eggs with caviar
Boil eggs, peel and cut lengthwise into two parts. Put black or red caviar on the yolk, decorate with greens and serve.
Salads
Salad "Russian Forest"
Cut the fillet of boiled quail, chicken or any meat into thin slices, pickled or fresh cucumbers, peeled apple, boiled potatoes and hard-boiled quail eggs. Mix, season with sour cream or mayonnaise, salt to taste, you can add lemon juice or vinegar, sprinkle lightly with powdered sugar. For decoration, make "fungi" from hard quail eggs and red-skinned apple slices, stick sprigs of parsley or dill between them.
Salad with ham
12-15 quail eggs,
100 g sausage, ham or smoked fish,
1 pickled cucumber
1 cup green peas
2 potatoes
200 g sour cream or mayonnaise,
1 teaspoon hot sauce
salt, dill, parsley leaves.
Cut the products into small cubes, mix with sour cream or mayonnaise, add seasoning to taste. Top the salad with finely chopped herbs and grated cheese.
|
Quail rearing
General information
Common quail is a bird of the pheasant family, chicken order. It is the smallest representative of the chicken order. The length of its body is 16 - 20 cm, weight 80 -150 g. The color of the plumage is brownish - brown, with light spots and strokes. In males, the color of the goiter and around the eyes is red, in females it is lighter.
Common quail is common in Europe, Africa and Southwest Asia. In Russia, it lives on the territory from the Black Sea to Lake Baikal. It is an object of hunting. Inhabits popyas, meadows, plains and mountains.
Birds are very shy and it is very difficult to notice them in nature. They nest in open areas with developed grass cover. As a rule, the nest - a small depression in the ground - is found and equipped by the female herself. She also incubates the eggs and protects the chicks for the first days after hatching. In one clutch there are from 8 to 24 speckled, yellow-brown eggs, weighing 10-12 g each. The chicks hatch in 17-18 days and as soon as they dry out, they immediately begin to peck at the food. They grow very fast. After two weeks, they acquire a feather cover and are already starting to try to fly from place to place, and by one and a half to two months they become completely adult independent birds. Common quail is perhaps the only migratory bird among chickens. With the onset of cold weather, it flies south.
In addition to the common quail, it is also called the European quail, and the mute or Japanese quail (Coturnix Japonica) also lives on the territory of Russia. It was domesticated in Japan in the late 19th and early 20th centuries and is the main bird on quail farms.
At present, several breeds of Japanese quail have been obtained through breeding: marbled, pharaoh, etc., which are bred with a chain for the production of eggs and meat, both at home and on an industrial scale.
The live weight of domestic quail males is about 110 g, females up to 150 g. Japanese domestic quails begin to lay eggs at the age of 50 - 60 days (for comparison, chickens begin to lay eggs no earlier than after 180 - 210 days). Each quail can lay up to 300 or more tasty and healthy eggs per year, each of which weighs 10-14g. The production of quail eggs is cheaper than chicken eggs, and quail breeding is the most profitable poultry farming. A female quail with a live weight of 125 g, egg production of 250 - 300 eggs has an egg mass of 20 - 24 times more than the bird itself (for chickens, 8 times). In addition, quails serve as "suppliers" of high-quality meat, which is considered a dietary product. No wonder in Russia quail dishes were considered royal food.
In the breeding chains of domestic quail breeds in many countries since the middle of the 20th century. specialized quail-breeding farms (farms) have been created, the profitability of which is quite high. Even specialized breeds of Japanese quail of different directions have been bred - egg-laying and broiler (meat).
Broiler quails quickly reach a mass of up to 200 - 250 g, while the mass of egg-laying birds rarely exceeds 150 - 180 g.
Quail eggs are superior in many nutrients to chicken eggs. Five quail eggs, equal in weight to one chicken, contain 5 times more potassium, 4.5 times more iron, 2.5 times more vitamins B1 and B2. Much more vitamin A, nicotinic acid, phosphorus, copper, cobalt, limiting and other amino acids in quail eggs. Quails have more protein in their eggs than other brood birds. For example, in chickens, 55.8% of protein will be held in an egg, in quails - 60%. In most brood birds, the egg shell is more than 10% of the mass of the entire egg, in quails - only 7.2%. The shell of quail eggs is pigmented, very fragile, but has a strong and elastic undershell film. The color of the shell of quail eggs varies from very dark, yellow-brown to pure white. The density of quail eggs is less than the density of chicken eggs, which is obviously due to the lower relative mass of the shell.
Quail eggs are a concentrated biological set of substances necessary for a person, these are real health ampoules. There is evidence in the literature that in ancient times, quail eggs and meat were used in oriental folk medicine. This was one of the reasons for the domestication and selection of quails in Japan. Even in the time of the pharaohs in Egypt, medicinal properties were attributed to quail meat. In Japan, raw quail eggs mixed with orange juice are still used to treat asthma.
Quail eggs are a valuable food product that can be recommended in the diet of children and adults with a number of diseases. They do not cause allergic phenomena even in those people for whom chicken eggs are contraindicated. In Central Asia, it is believed that the quail brings wealth and prosperity to the house where it is kept in a cage. In addition, quails are valued for their beautiful songs. In the old days, in the Kursk province they even kept domestic singing quails and for their songs they were valued no lower than the Kursk nightingales.
Breeds and varieties of domestic quail
Today, people are increasingly striving to switch to their own cultivation, both vegetables, fruits, and animals. And if everyone knows how to grow and care for chickens, then there are many nuances in breeding quails that should be considered. Not only are quail eggs and meat several times healthier than chicken meat, but quails also take up much less space.
To breed quails, you do not need to build a whole chicken coop. Fifty of these birds are easily placed on an area of 1 square meter.
Conditions for keeping birds
Regardless of the place in which you will be breeding and raising quails. There are several factors to be observed.
The key to the well-being of birds is a well-chosen temperature regime. The air temperature must be stable, around 20°C. If this is not the case, then in hot weather the bird will lose its plumage and stop rushing. If suddenly the temperature drops below 8 ° C, then this can generally lead to death.
The second, but no less important condition for growing quails is a comfortable cage. You can easily make your own or buy it.
But you need to remember that the cage should be just for quails. In no case should you use the cages of your former pets (parrots, canaries, etc.) for them.
A cage for breeding quails must meet certain requirements. For instance:
- all elements of the cage must be metal or steel;
- all feeding devices (drinkers, feeders) should be outside the cages, usually they are placed on the front wall of the cage and the birds stick their heads between the bars to refresh themselves;
- the height of the cage should not be more than 25 cm, because if it is higher, then the birds can jump high, which will inevitably injure their heads;
- to collect eggs, the bottom of the cage should be equipped with a special tray for receiving;
- do not forget to arrange a litter tray for the birds, this will help keep the cage cleaner.
Experienced farmers advise choosing a cage area with a calculation of 0.2 m for 10 quails. If there are fewer birds, they may stop rushing.
Growing in an incubator
If, when buying quails, your main goal was to breed them, then it would be much more expedient to acquire an incubator. With it, you can hatch quails from eggs on your own, without the help of an adult quail.
As for rearing, those who have already tried to take chickens out of an incubator at least once know that even in the newest devices there is a minimum temperature fluctuation, which is why eggs around the edges constantly need to be shifted. And thanks to the small size of the quail eggs, they all fit in the middle of the platform so you don't have to swap them. Thanks to this, you can buy any inexpensive incubator to breed quails, and it will work great.
It is advised to buy eggs for the incubator only fresh (not older than 5 days) and preferably from farmers. In the process of incubation of quail eggs, you will not find many differences from chicken ones. Is it just a deadline, a quail egg should be kept up to 17 days, turning up to 6 times a day. For the first one and a half weeks of incubation, it is desirable to maintain a stable temperature - about 39 ° C. And then the temperature should be reduced by one degree, to 38 ° C. The day before the chicks hatch, the recommended temperature in the incubator is 37 °C.
Hatching quail has one big advantage. Unlike chicks, all chicks hatch at the same time. If there are quails that hatched an average of 12 hours later than the rest, try to get rid of them, because according to statistics they die in the first week. And in this way, you will save yourself both time and nerves.
Quail feeding
The breeding and feeding technology for quail is almost the same as for chickens. The main difference is only the feeding vessels. For quails, it is desirable to install small containers with low sides for feeding and a vacuum drinker. If the drinker is too large or deep, inexperienced chicks may drown in it. At the beginning of the life of babies, a special place in their diet should be given to a hard-boiled and chopped egg. Later, it will be possible to gradually introduce specialized feed into their diet.
Usually small quails are moved to a specialized container for warming. In order not to constantly change their habitat, you can simply move 20-day-old chicks slowly into a cage for adult birds, but first it should be insulated and ventilation taken care of.
Diet
Basically, cereals such as oats, corn, barley, etc. are used to feed quails. A complete feeding technology consists in providing the birds with a balanced and proper diet (you can find out about the average feed consumption per laying hen).
The main source of health for birds is corn. Due to the high percentage of starch content, corn has a fairly high energy value, which allows the birds to saturate faster and for a longer time. But it should be remembered that it contains few vitamins, so it is advisable to add meal or fishmeal along with corn.
It is impossible not to note the usefulness of oats. Due to the high content of vitamins, this food is dietary and is introduced into complementary foods for quails even in the first weeks, however, it is pre-crushed and cleaned. Millet has practically the same properties, but its energy value is slightly higher.

Legumes are an excellent plant food for quails. They contain a large amount of proteins necessary for growth and development, but a smaller amount of vitamins and fats. When feeding, you can use peas, soybeans, lentils and other legumes.
As useful additives, you can give quails a small amount of flax or hemp seeds. But be sure to keep an eye on them.
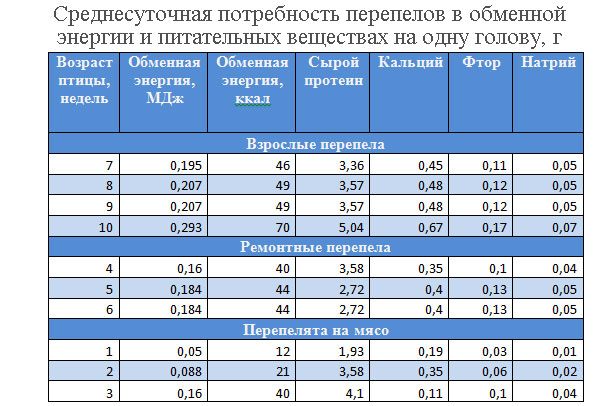
For successful and efficient keeping of birds, it is imperative to observe the temperature regime, proper lighting, and also monitor the absence of unnecessary irritants that can disturb pets. Also, special attention should be paid to the feed. It should be balanced and contain a high percentage of protein.
In order for quails to actively rush, they do not need a male at all. Birds just need to provide comfortable conditions for living.
If you want to keep quails for decorative purposes, then it is advisable to settle the birds in pairs or small groups.